p.1623
p.1629
p.1634
p.1641
p.1647
p.1652
p.1657
p.1661
p.1665
Simulation on NOx Generation of RSP Calciner for Cement Production
Abstract:
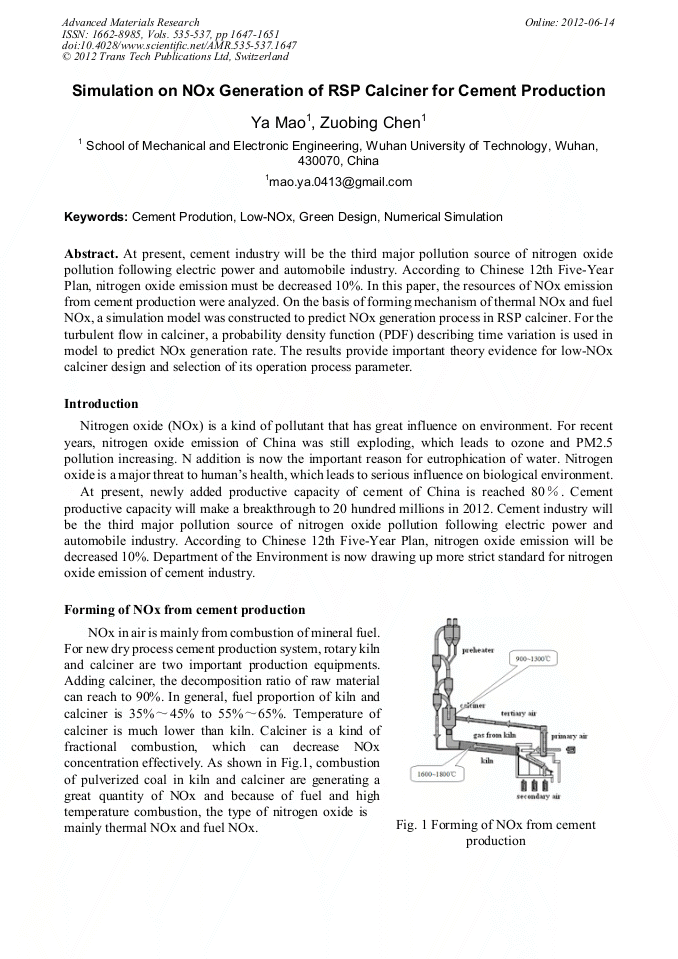
At present, cement industry will be the third major pollution source of nitrogen oxide pollution following electric power and automobile industry. According to Chinese 12th Five-Year Plan, nitrogen oxide emission must be decreased 10%. In this paper, the resources of NOx emission from cement production were analyzed. On the basis of forming mechanism of thermal NOx and fuel NOx, a simulation model was constructed to predict NOx generation process in RSP calciner. For the turbulent flow in calciner, a probability density function (PDF) describing time variation is used in model to predict NOx generation rate. The results provide important theory evidence for low-NOx calciner design and selection of its operation process parameter.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1647-1651
Citation:
Online since:
June 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: