p.1133
p.1139
p.1143
p.1147
p.1151
p.1156
p.1166
p.1172
p.1177
Energy-Saving Analysis for Power System Reactive Power Compensation
Abstract:
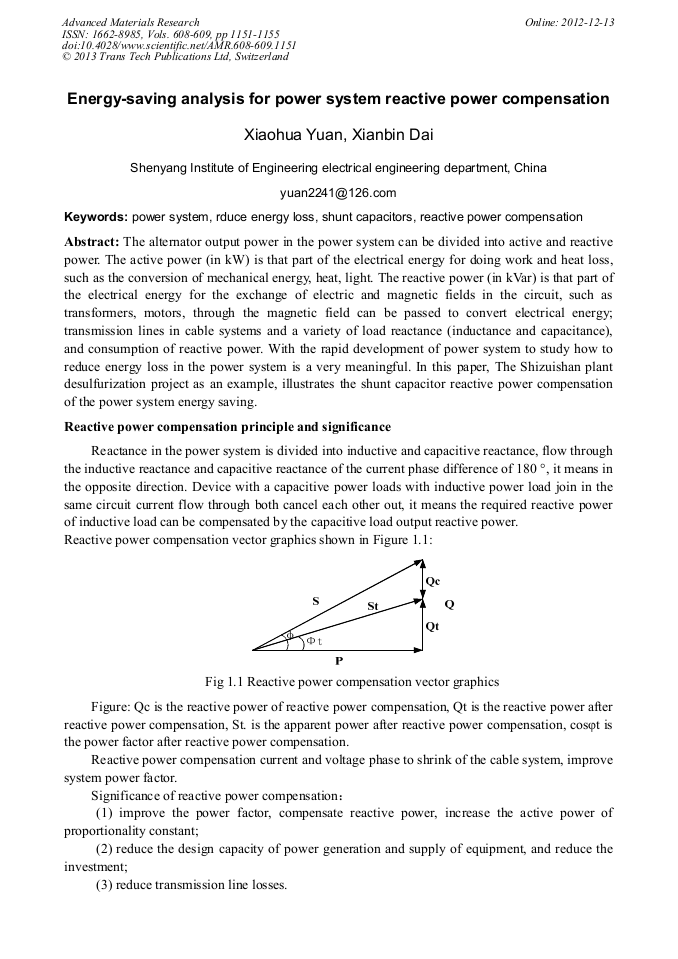
The alternator output power in the power system can be divided into active and reactive power. The active power (in kW) is that part of the electrical energy for doing work and heat loss, such as the conversion of mechanical energy, heat, light. The reactive power (in kVar) is that part of the electrical energy for the exchange of electric and magnetic fields in the circuit, such as transformers, motors, through the magnetic field can be passed to convert electrical energy; transmission lines in cable systems and a variety of load reactance (inductance and capacitance), and consumption of reactive power. With the rapid development of power system to study how to reduce energy loss in the power system is a very meaningful. In this paper, The Shizuishan plant desulfurization project as an example, illustrates the shunt capacitor reactive power compensation of the power system energy saving.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1151-1155
Citation:
Online since:
December 2012
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: