p.216
p.221
p.225
p.230
p.235
p.239
p.243
p.247
p.251
Research on Movement Stability of Robotic Arm Driven by Antagonistic Pneumatic Artificial Muscle with Mechanical Properties
Abstract:
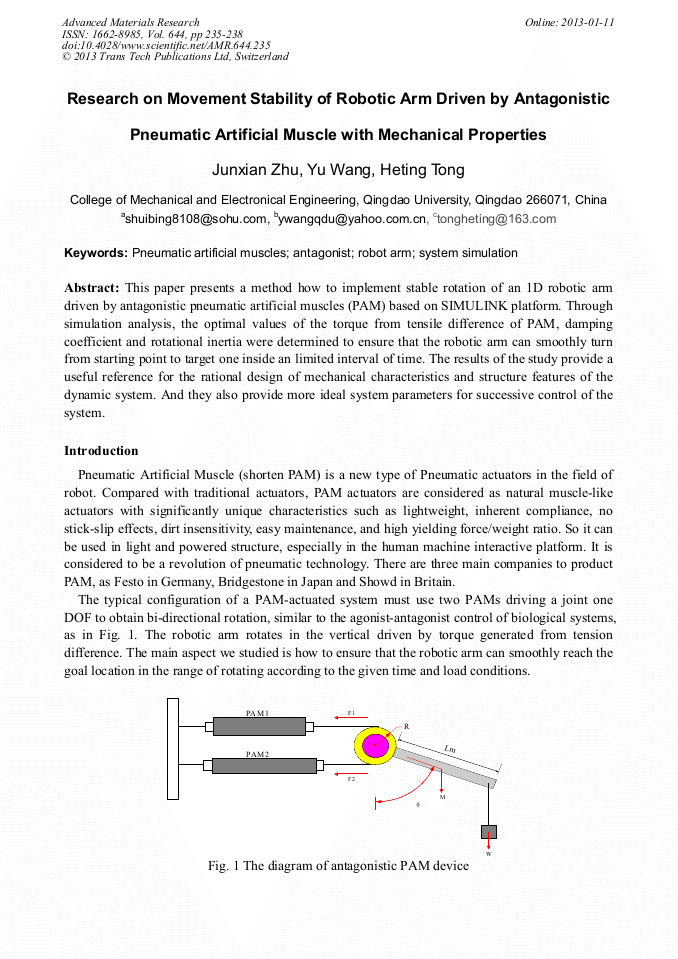
This paper presents a method how to implement stable rotation of an 1D robotic arm driven by antagonistic pneumatic artificial muscles (PAM) based on SIMULINK platform. Through simulation analysis, the optimal values of the torque from tensile difference of PAM, damping coefficient and rotational inertia were determined to ensure that the robotic arm can smoothly turn from starting point to target one inside an limited interval of time. The results of the study provide a useful reference for the rational design of mechanical characteristics and structure features of the dynamic system. And they also provide more ideal system parameters for successive control of the system.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
235-238
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
January 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: