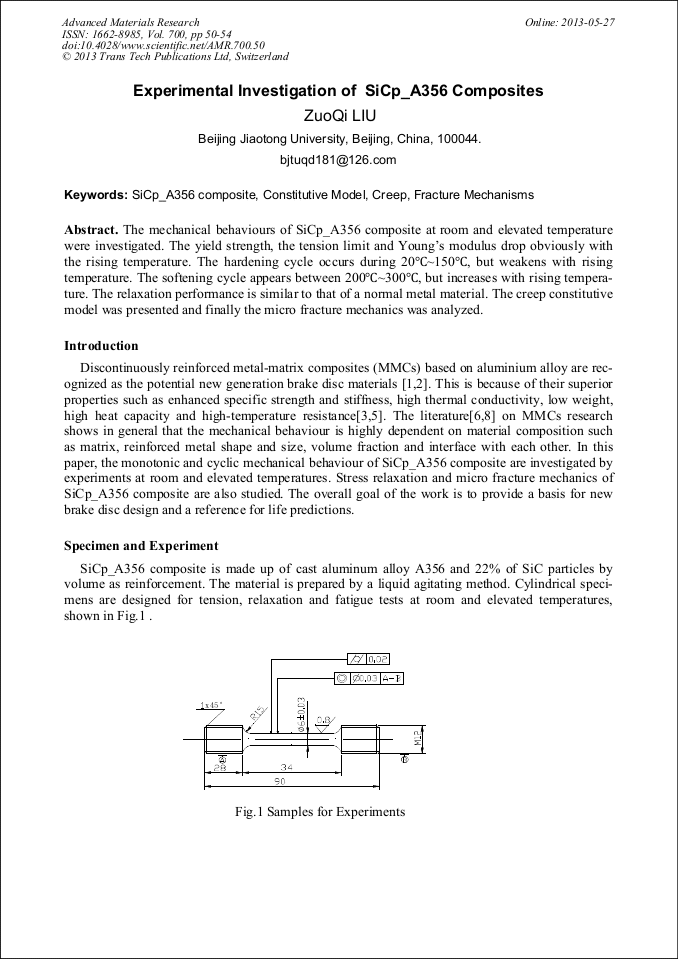
[1]
J. Yamabe, M. Takagi, T.Matsui, etc.. Development of disc brake rotors for trucks with high thermal fatigue strength. SAE of Japan, 23, 105-112, 2002.
DOI: 10.1016/s0389-4304(01)00153-9
Google Scholar
[2]
M. Kuboto, K. Hamabe, Y. Nakazono etc.. Development of a lightweight brake disc rotor :a design approach for achieving an optimum thermal, vibration and weight balance, JSAE, 21, 349-355, 2000.
DOI: 10.1016/s0389-4304(00)00050-3
Google Scholar
[3]
N. Han, Z. Wang, G. Zhang, Low-cycle fatigue behaviour of a particulate SiC/2024Al composite at ambient and elevated temperature. Composites Science and Technology, 59, 147-155, 1999.
DOI: 10.1016/s0266-3538(97)00118-8
Google Scholar
[4]
S. Roberts, J. Kusiak, Y. Liu etc. Prediction of damage evolution in forged aluminum metal matrix composites using a neural network approach, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 80-81, 507-512, 1998.
DOI: 10.1016/s0924-0136(98)00153-8
Google Scholar
[5]
J. LLorca, High temperature fatigue of discontinuously- reinforced metal–matrix composites, International Journal of Fatigue, 2-4, 233-240, 2002.
DOI: 10.1016/s0142-1123(01)00077-9
Google Scholar
[6]
N. Han, Z. Wang. Effect of reinforcement size on the elevated temperature tensile properties and low-cycle fatigue behavior of a particulate SiC/Al composite, Composites Science and Technology, 57, 1491-1499, 1999.
DOI: 10.1016/s0266-3538(97)00072-9
Google Scholar
[7]
C. Perng, J. Hwang, J. Doong, High strain rate tensile properties of an (Al2O3 particles)-(Al alloy 6061-T6) metal matrix composite, Materials Science and Engineering, 1-2, 213-221, 1993.
DOI: 10.1016/0921-5093(93)90408-7
Google Scholar
[8]
T. Srivatsan, M. Hajri, V. Vasudevan, Cyclic plastic strain response and fracture behavior of 2009 aluminum alloy metal-matrix composite, International Journal of Fatigue, 4, 357-371, 2005.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2004.08.009
Google Scholar
[9]
A. Mukherjee, J. Bird, Dorn J E, Trans ASM, 62-155, 1969.
Google Scholar