p.1140
p.1146
p.1150
p.1154
p.1159
p.1163
p.1167
p.1171
p.1175
Research on Aluminum Electrolytic Multi-Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Immune Genetic Algorithm
Abstract:
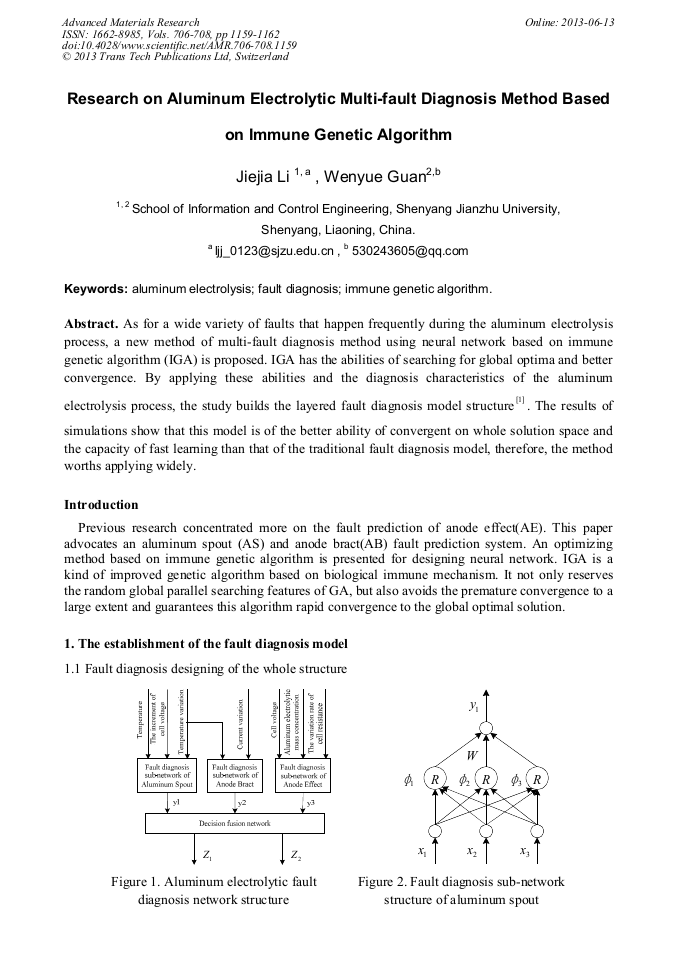
As for a wide variety of faults that happen frequently during the aluminum electrolysis process, a new method of multi-fault diagnosis method using neural network based on immune genetic algorithm (IGA) is proposed. IGA has the abilities of searching for global optima and better convergence. By applying these abilities and the diagnosis characteristics of the aluminum electrolysis process, the study builds the layered fault diagnosis model structure . The results of simulations show that this model is of the better ability of convergent on whole solution space and the capacity of fast learning than that of the traditional fault diagnosis model, therefore, the method worths applying widely.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1159-1162
Citation:
Online since:
June 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: