p.3613
p.3622
p.3627
p.3633
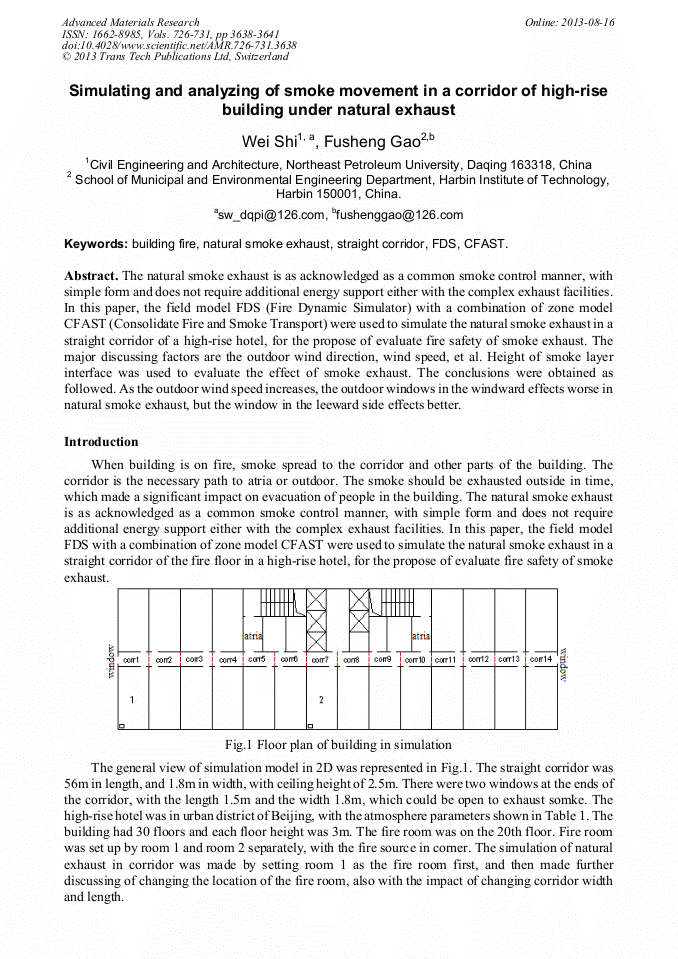
p.3638
p.3642
p.3646
p.3653
p.3657
Simulating and Analyzing of Smoke Movement in a Corridor of High-Rise Building under Natural Exhaust
Abstract:
The natural smoke exhaust is as acknowledged as a common smoke control manner, with simple form and does not require additional energy support either with the complex exhaust facilities. In this paper, the field model FDS (Fire Dynamic Simulator) with a combination of zone model CFAST (Consolidate Fire and Smoke Transport) were used to simulate the natural smoke exhaust in a straight corridor of a high-rise hotel, for the propose of evaluate fire safety of smoke exhaust. The major discussing factors are the outdoor wind direction, wind speed, et al. Height of smoke layer interface was used to evaluate the effect of smoke exhaust. The conclusions were obtained as followed. As the outdoor wind speed increases, the outdoor windows in the windward effects worse in natural smoke exhaust, but the window in the leeward side effects better.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
3638-3641
Citation:
Online since:
August 2013
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: