p.747
p.752
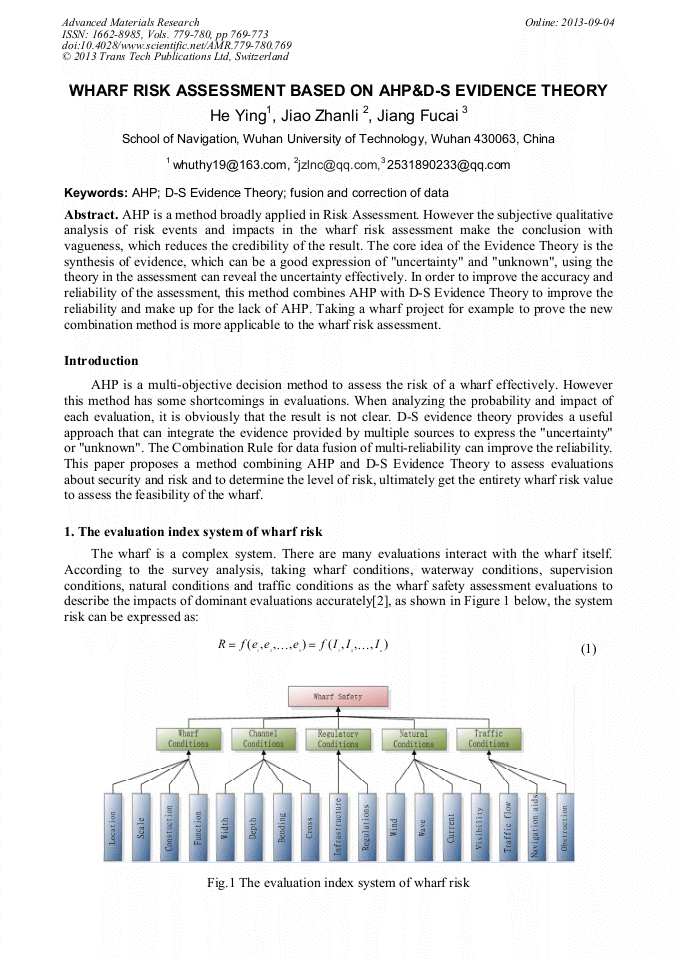
p.757
p.763
p.769
p.774
p.779
p.784
p.788
Wharf Risk Assessment Based on AHP&D-S Evidence Theory
Abstract:
AHP is a method broadly applied in Risk Assessment. However this method has some shortcomings in evaluations. The subjective qualitative analysis of risk events and impacts in the wharf risk assessment make the conclusion with vagueness, which reduces the credibility of the result. The core idea of the Evidence Theory is the synthesis of evidence, which can be a good expression of "uncertainty" and "unknown", using the theory in the assessment can reveal the uncertainty effectively. In order to improve the accuracy and reliability of the assessment, this method combines AHP with D-S Evidence Theory, in which the D-S Evidence Theory applied to fuse and correct the expert rating data for determine-making of the wharf risk and AHP used to establish the system of assessment and determine the value. The Combination Rule for data fusion of multi- reliability can improve the reliability and make up for the lack of AHP. Through correction and data fusion by Synthetic Formula, the high support reviews get higher credibility, the low support reviews get lower credibility after synthesis, the polarization phenomenon lets the result more realistic and accurate. Taking a wharf project for example to prove the new combination method is more applicable to the wharf risk assessment.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
769-773
Citation:
Online since:
September 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: