p.178
p.182
p.187
p.192
p.198
p.202
p.207
p.212
p.217
Development of Integrated Experiment Program for Marine Concrete Durability
Abstract:
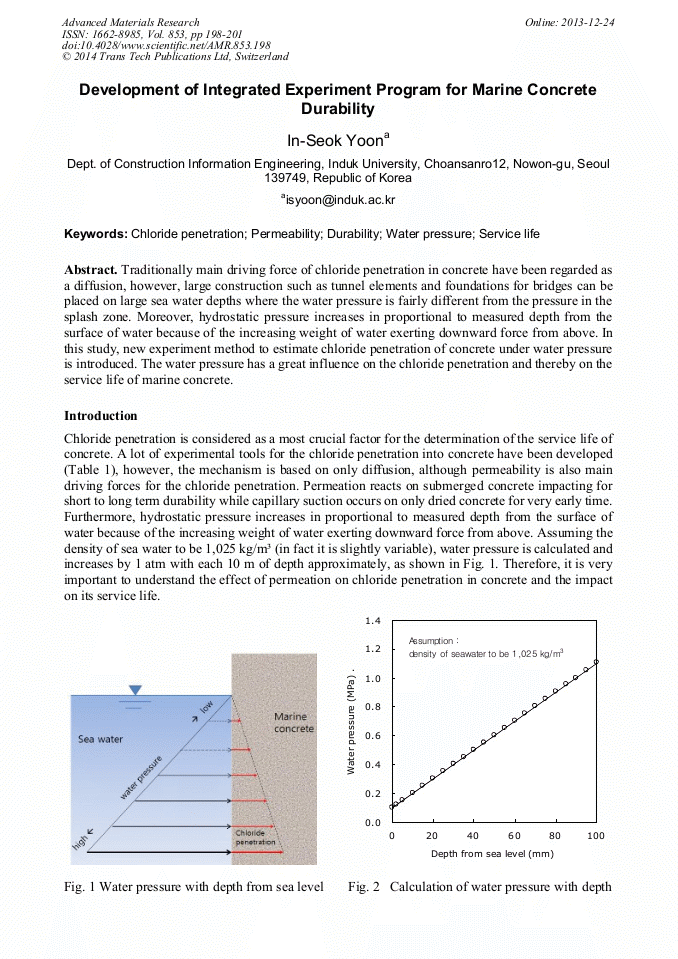
Traditionally main driving force of chloride penetration in concrete have been regarded as a diffusion, however, large construction such as tunnel elements and foundations for bridges can be placed on large sea water depths where the water pressure is fairly different from the pressure in the splash zone. Moreover, hydrostatic pressure increases in proportional to measured depth from the surface of water because of the increasing weight of water exerting downward force from above. In this study, new experiment method to estimate chloride penetration of concrete under water pressure is introduced. The water pressure has a great influence on the chloride penetration and thereby on the service life of marine concrete.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
198-201
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
December 2013
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: