p.1729
p.1734
p.1739
p.1744
p.1748
p.1754
p.1761
p.1767
p.1771
Thermoeconomic Analysis of Air Conditioning Systems
Abstract:
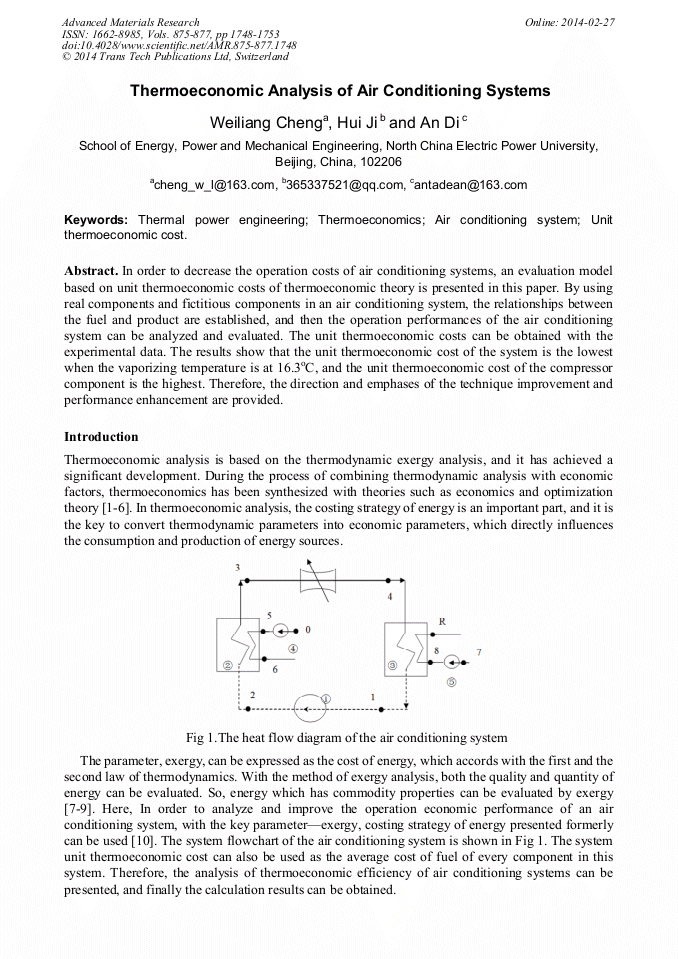
In order to decrease the operation costs of air conditioning systems, an evaluation model based on unit thermoeconomic costs of thermoeconomic theory is presented in this paper. By using real components and fictitious components in an air conditioning system, the relationships between the fuel and product are established, and then the operation performances of the air conditioning system can be analyzed and evaluated. The unit thermoeconomic costs can be obtained with the experimental data. The results show that the unit thermoeconomic cost of the system is the lowest when the vaporizing temperature is at 16.3°C, and the unit thermoeconomic cost of the compressor component is the highest. Therefore, the direction and emphases of the technique improvement and performance enhancement are provided.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1748-1753
Citation:
Online since:
February 2014
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: