p.1464
p.1471
p.1479
p.1483
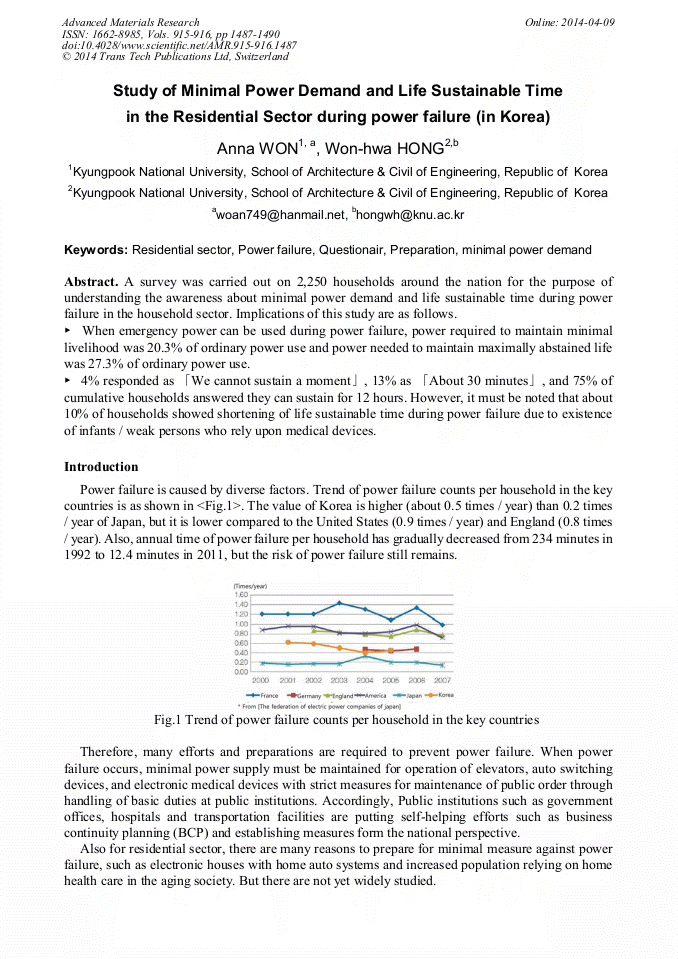
p.1487
p.1491
p.1495
p.1500
p.1504
Study of Minimal Power Demand and Life Sustainable Time in the Residential Sector during Power Failure (in Korea)
Abstract:
A survey was carried out on 2,250 households around the nation for the purpose of understanding the awareness about minimal power demand and life sustainable time during power failure in the household sector. Implications of this study are as follows. When emergency power can be used during power failure, power required to maintain minimal livelihood was 20.3% of ordinary power use and power needed to maintain maximally abstained life was 27.3% of ordinary power use. 4% responded as We cannot sustain a moment, 13% as About 30 minutes, and 75% of cumulative households answered they can sustain for 12 hours. However, it must be noted that about 10% of households showed shortening of life sustainable time during power failure due to existence of infants / weak persons who rely upon medical devices.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1487-1490
Citation:
Online since:
April 2014
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: