p.852
p.858
p.862
p.866
p.870
p.874
p.878
p.882
p.887
Simulation Study on Effects of Ignition Time on Particle Emission for GDI Engine
Abstract:
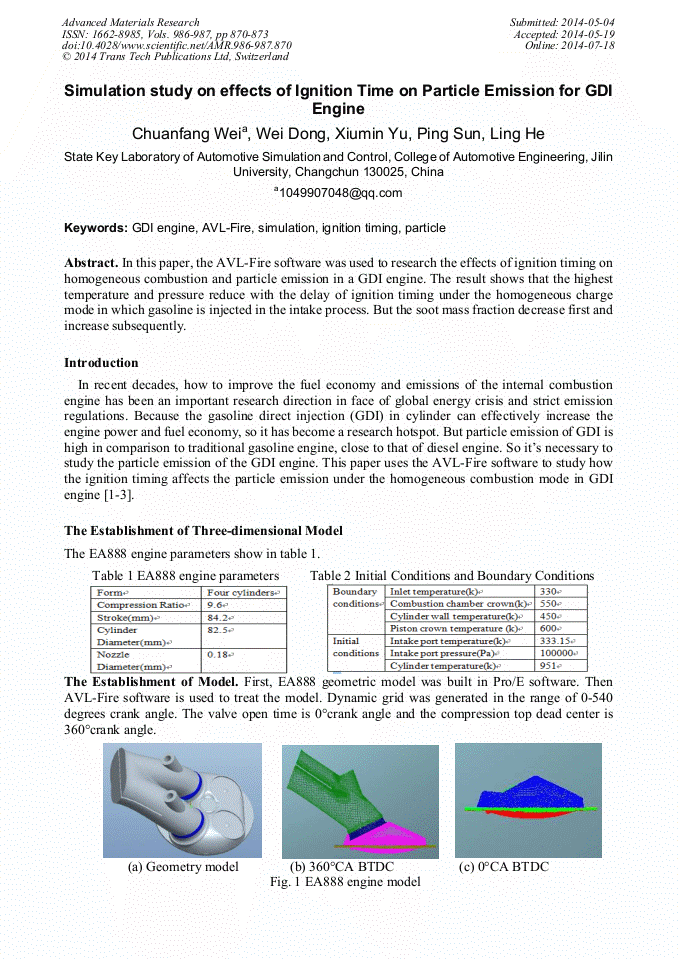
In this paper, the AVL-Fire software was used to research the effects of ignition timing on homogeneous combustion and particle emission in a GDI engine. The result shows that the highest temperature and pressure reduce with the delay of ignition timing under the homogeneous charge mode in which gasoline is injected in the intake process. But the soot mass fraction decrease first and increase subsequently.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
870-873
Citation:
Online since:
July 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: