p.1429
p.1435
p.1444
p.1450
p.1456
p.1462
p.1469
p.1475
p.1483
Structure and Properties of Heterophase Nanostructured Ceramics
Abstract:
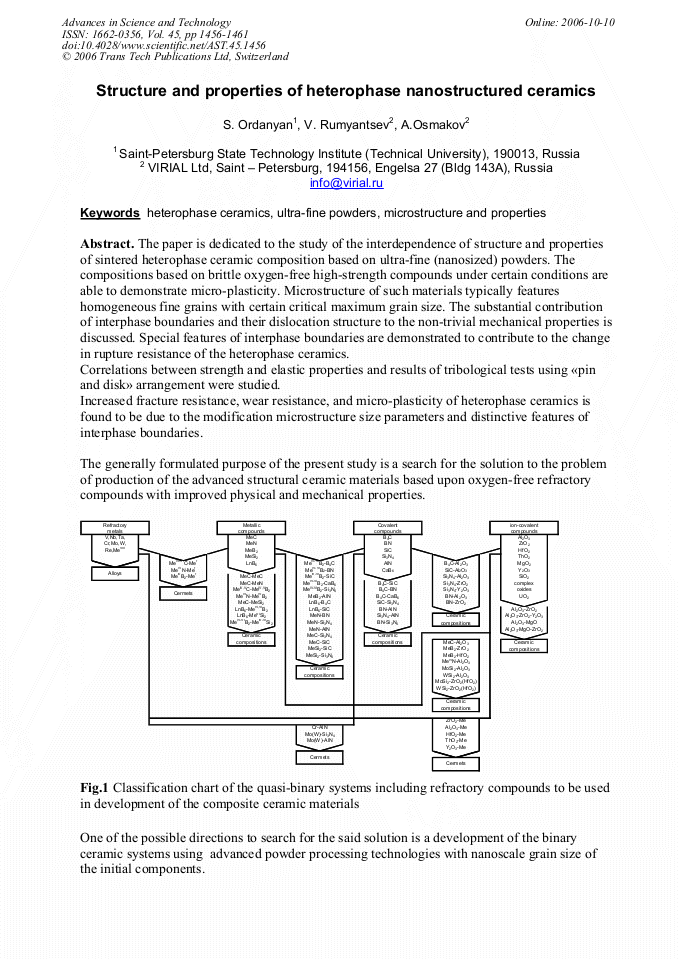
The paper is dedicated to the study of the interdependence of structure and properties of sintered heterophase ceramic composition based on ultra-fine (nanosized) powders. The compositions based on brittle oxygen-free high-strength compounds under certain conditions are able to demonstrate micro-plasticity. Microstructure of such materials typically features homogeneous fine grains with certain critical maximum grain size. The substantial contribution of interphase boundaries and their dislocation structure to the non-trivial mechanical properties is discussed. Special features of interphase boundaries are demonstrated to contribute to the change in rupture resistance of the heterophase ceramics. Correlations between strength and elastic properties and results of tribological tests using «pin and disk» arrangement were studied. Increased fracture resistance, wear resistance, and micro-plasticity of heterophase ceramics is found to be due to the modification microstructure size parameters and distinctive features of interphase boundaries. The generally formulated purpose of the present study is a search for the solution to the problem of production of the advanced structural ceramic materials based upon oxygen-free refractory compounds with improved physical and mechanical properties.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1456-1461
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
October 2006
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2006 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: