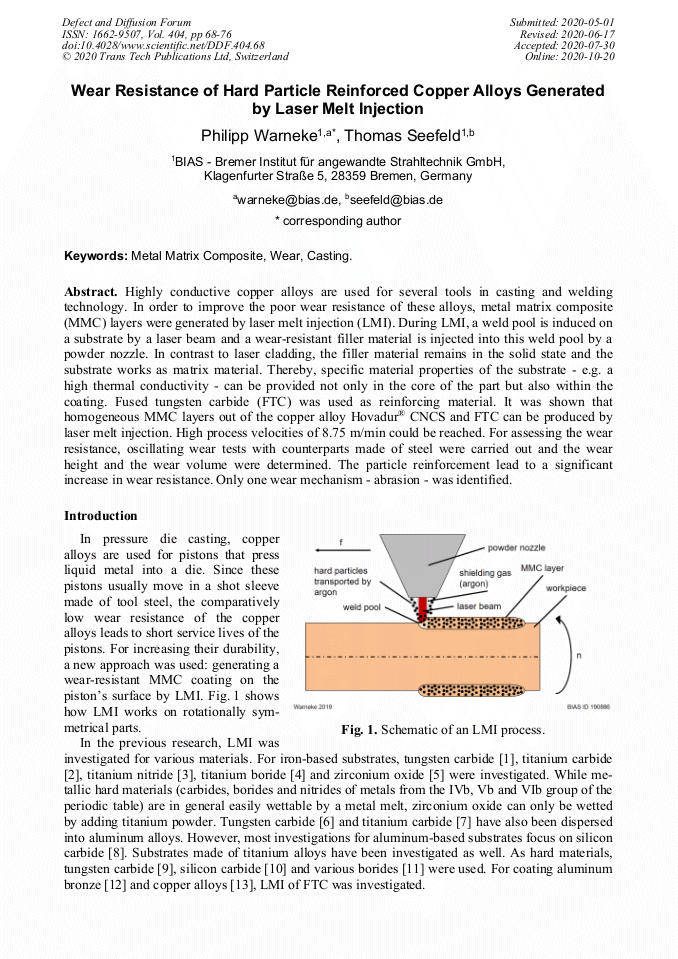
[1]
A.M. Do Nascimento, V. Ocelík, M.C.F. Ierardi, J.T.M. de Hosson, Wear resistance of WCp/Duplex Stainless Steel metal matrix composite layers prepared by laser melt injection, Surface and Coatings Technology 202 (2008) 4758–4765.
DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.04.061
Google Scholar
[2]
J.D. Ayers, T.R. Tucker, Particulate-TiC-hardened steel surfaces by laser melt injection, Thin Solid Films (1980) 201–207.
DOI: 10.1016/0040-6090(80)90352-1
Google Scholar
[3]
M. Cabeza, G. Castro, P. Merino, G. Pena, M. Roman, A study of laser melt injection of TiN particles to repair maraging tool steels, Surf. Interface Anal. 46 (2014) 861–864.
DOI: 10.1002/sia.5373
Google Scholar
[4]
K. Hilgenberg, K. Steinhoff, Texturing of skin-pass rolls by pulsed laser dispersing, Journal of Materials Processing Technology 225 (2015) 84–92.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.05.027
Google Scholar
[5]
M. Deutschmann, Lasergestützte Herstellung von Keramik-Stahl-Werkstoffverbundschichten für Werkzeuge der Blechumformung. Dissertation, Hannover, (2007).
Google Scholar
[6]
R. Jendrzejewski, K. van Acker, D. Vanhoyweghen, G. Śliwiński, Metal matrix composite production by means of laser dispersing of SiC and WC powder in Al alloy, Applied Surface Science 255 (2009) 5584–5587.
DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.09.048
Google Scholar
[7]
O. Velde, A. Techel, R. Grundmann, Suppression of the development of pores during laser-induced surface dispersion of TiC into aluminium, by means of a static magnetic field, Surface and Coatings Technology 150 (2002) 170–176.
DOI: 10.1016/s0257-8972(01)01531-6
Google Scholar
[8]
M. Student, H. Pokhmurska, K. Zadorozhna, A. Dzyubyk, I. Khomych, Structure and wear resistance of aluminium alloys coated with surface layer laser-modified by silicon carbide, Ukrainian Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science 4 (2018) 49–57.
DOI: 10.23939/ujmems2018.01.049
Google Scholar
[9]
J.A. Vreeling, V. Ocelik, J.T.M. de Hosson, Ti–6Al–4V strengthened by laser melt injection of WCp particles, Acta Materialia (2002) 4913–4924.
DOI: 10.1016/s1359-6454(02)00366-x
Google Scholar
[10]
Y.T. Pei, V. Ocelik, J.T.M. de Hosson, SiCp /Ti6Al4V functionally graded materials produced by laser melt injection, Acta Materialia (2002) 2035–(2051).
DOI: 10.1016/s1359-6454(02)00049-6
Google Scholar
[11]
G. Kolbe, Beitrag zur Erhöhung der Verschleißbeständigkeit von Bauteilen aus TiAl5V4 durch Dispergieren/Legieren mit Diboriden. Dissertation, Chemnitz, (2004).
Google Scholar
[12]
H. Freiße, V. Hohenäcker, T. Seefeld, F. Vollertsen, Laser generated tool surface out of metal matrix composite, Dry Metal Forming Open Access Journal 3 (2017) 41–44.
Google Scholar
[13]
P. Warneke, T. Seefeld, High-Speed Laser Melt Injection of Tungsten Carbide in Highly Conductive Copper Alloys, KEM 809 (2019) 94–99.
DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.809.94
Google Scholar
[14]
T. Schopphoven, A. Gasser, G. Backes, EHLA: Extreme High-Speed Laser Material Deposition, Laser Technik Journal 14 (2017) 26–29.
DOI: 10.1002/latj.201700020
Google Scholar
[15]
T. Molitor, GTV Top Speed Cladding, als wirtschaftliche Alternative zum Hartverchromen, Schweißen und Schneiden 70 (2018) 327–329.
Google Scholar
[16]
Innotech Laser GmbH, Ultra-High-Speed-Laser-Cladding, Lasermagazin (2018) 28–30.
Google Scholar
[17]
Schmelzmetall Deutschland, Werkstoffdatenblatt Hovadur® CNCS, 2014, https://www.schmelzmetall.com/fileadmin/downloads/hovadur/hovadur-cncs-de.pdf, accessed 23 April (2020).
DOI: 10.31399/asm.ad.cu0932
Google Scholar
[18]
Oerlikon Metco, Material Product Data Sheet Spherical Cast Tungsten Carbide Powder for Laser Cladding, 2016, https://www.oerlikon.com/metco/en/products-services/coating-materials/laser-pta-weld-overlay/laser-cladding/, accessed 23 April (2020).
Google Scholar
[19]
DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V., Hochleistungskeramik – Verfahren zur Prüfung keramischer Schichten – Teil 12: Schwingungs-Verschleißprüfung; Deutsche Fassung EN 1071-12:2010, (2010).
DOI: 10.31030/1552322
Google Scholar
[20]
F. Dausinger, Strahlwerkzeug Laser: Energieeinkopplung und Prozeßeffektivität. Habilitation, Stuttgart, (1995).
Google Scholar
[21]
J. Wilden, S. Jahn, N. Melahin, L. Rehfeldt, T. Luhn, S.-F. Goecke, E. Schmid, U. Berger, Löten als Schlüssel zum ressourcen- und energieeffizienten Fügen im Produktlebenszyklus, Schweißen und Schneiden 62 (2010) 264–277.
Google Scholar
[22]
S. Brust, Entwicklung abrasionsbeständiger Metallmatrix-Verbundwerkstoffe auf Eisenbasis mit ionisch-kovalenten Hartstoffen unter Betrachtung der Metall-Keramik-Interaktion. Dissertation, Bochum, (2017).
Google Scholar
[23]
H. Freiße, A. Bohlen, T. Seefeld, Determination of the particle content in laser melt injected tracks, Journal of Materials Processing Technology 267 (2019) 177–185.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.12.018
Google Scholar