p.1025
p.1028
p.1031
p.1034
p.1038
p.1041
p.1044
p.1047
p.1050
Improvement of Chemical Liquid Vaporized Infiltration Process for Fast Densification of Carbon/Carbon Composites
Abstract:
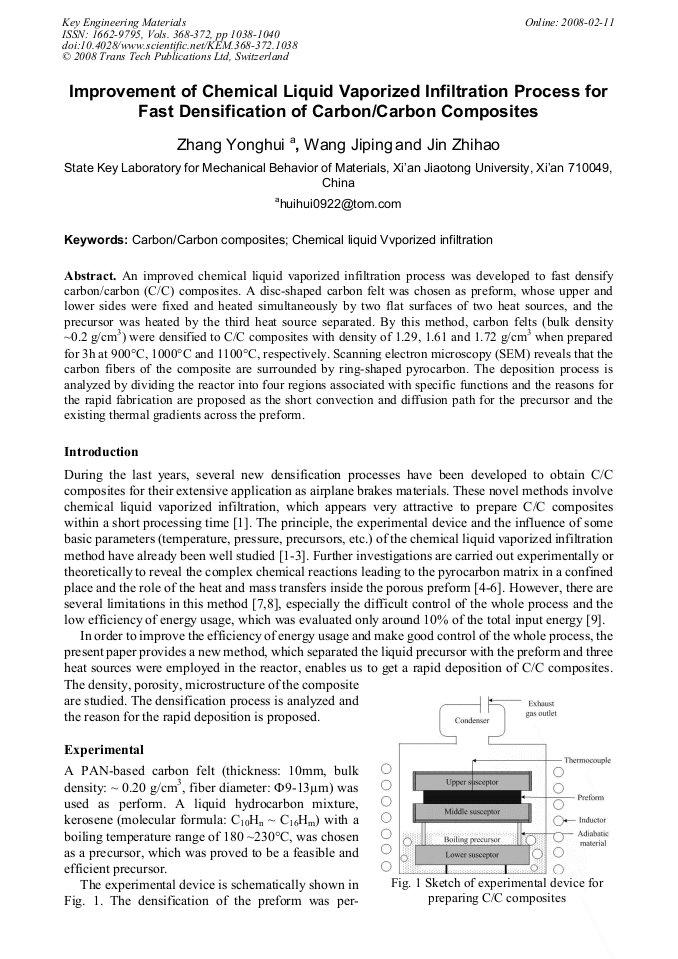
An improved chemical liquid vaporized infiltration process was developed to fast densify carbon/carbon (C/C) composites. A disc-shaped carbon felt was chosen as preform, whose upper and lower sides were fixed and heated simultaneously by two flat surfaces of two heat sources, and the precursor was heated by the third heat source separated. By this method, carbon felts (bulk density ~0.2 g/cm3) were densified to C/C composites with density of 1.29, 1.61 and 1.72 g/cm3 when prepared for 3h at 900°C, 1000°C and 1100°C, respectively. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) reveals that the carbon fibers of the composite are surrounded by ring-shaped pyrocarbon. The deposition process is analyzed by dividing the reactor into four regions associated with specific functions and the reasons for the rapid fabrication are proposed as the short convection and diffusion path for the precursor and the existing thermal gradients across the preform.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1038-1040
Citation:
Online since:
February 2008
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2008 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: