p.529
p.533
p.537
p.541
p.545
p.549
p.553
p.557
p.561
Effect of Micro-Climatic Condition on Durability Performance of Concrete
Abstract:
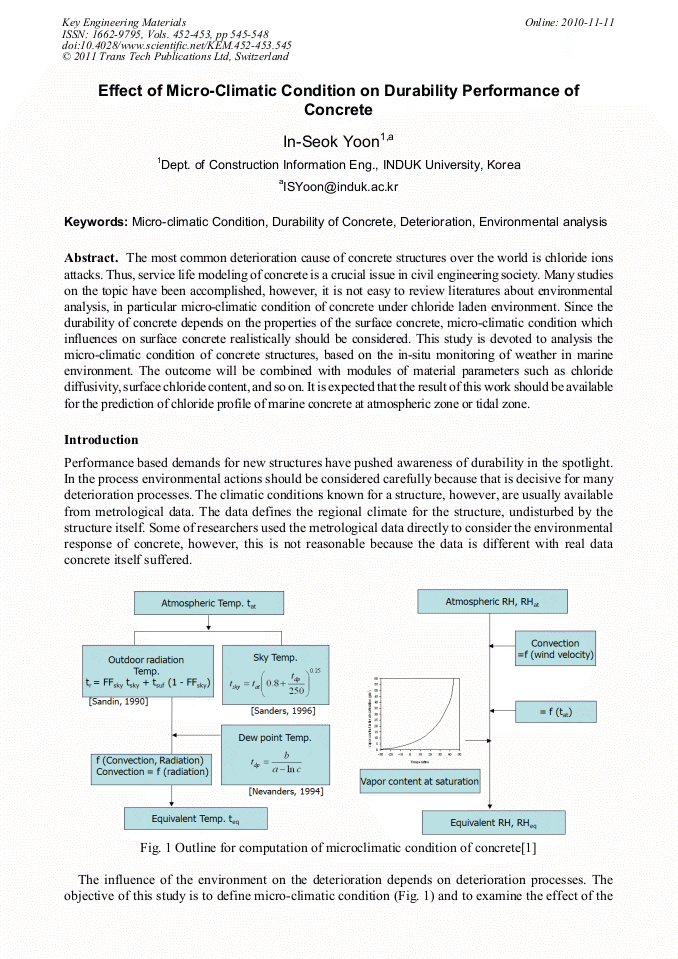
The most common deterioration cause of concrete structures over the world is chloride ions attacks. Thus, service life modeling of concrete is a crucial issue in civil engineering society. Many studies on the topic have been accomplished, however, it is not easy to review literatures about environmental analysis, in particular micro-climatic condition of concrete under chloride laden environment. Since the durability of concrete depends on the properties of the surface concrete, micro-climatic condition which influences on surface concrete realistically should be considered. This study is devoted to analysis the micro-climatic condition of concrete structures, based on the in-situ monitoring of weather in marine environment. The outcome will be combined with modules of material parameters such as chloride diffusivity, surface chloride content, and so on. It is expected that the result of this work should be available for the prediction of chloride profile of marine concrete at atmospheric zone or tidal zone.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
545-548
Citation:
Online since:
November 2010
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: