p.621
p.625
p.629
p.633
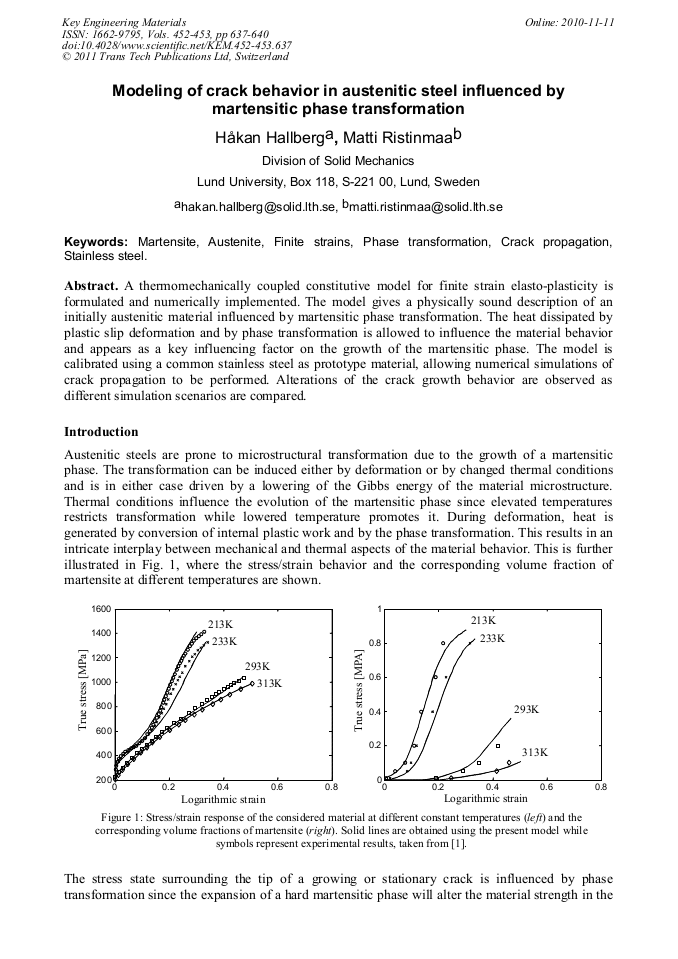
p.637
p.641
p.645
p.649
p.653
Modeling of Crack Behavior in Austenitic Steel Influenced by Martensitic Phase Transformation
Abstract:
A thermomechanically coupled constitutive model for finite strain elasto-plasticity is formulated and numerically implemented. The model gives a physically sound description of an initially austenitic material influenced by martensitic phase transformation. The heat dissipated by plastic slip deformation and by phase transformation is allowed to influence the material behavior and appears as a key influencing factor on the growth of the martensitic phase. The model is calibrated using a common stainless steel as prototype material, allowing numerical simulations of crack propagation to be performed. Alterations of the crack growth behavior are observed as different simulation scenarios are compared.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
637-640
Citation:
Online since:
November 2010
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: