p.481
p.487
p.492
p.498
p.504
p.510
p.516
p.522
p.527
The Improvement of Removal Function in Local Wet Etching by Using Eccentric Rotation System
Abstract:
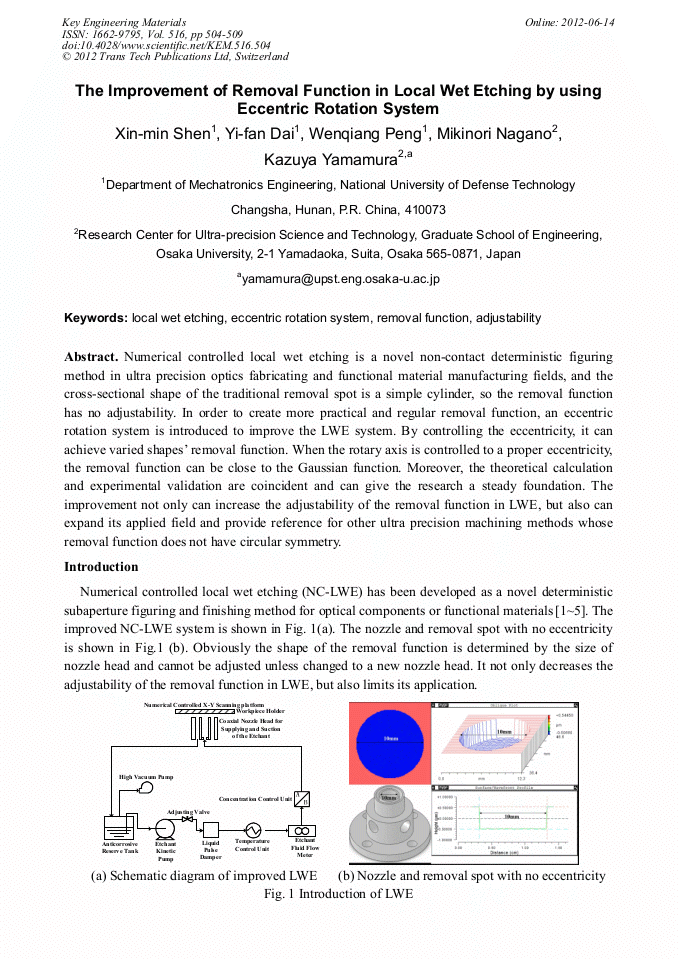
Numerical controlled local wet etching is a novel non-contact deterministic figuring method in ultra precision optics fabricating and functional material manufacturing fields, and the cross-sectional shape of the traditional removal spot is a simple cylinder, so the removal function has no adjustability. In order to create more practical and regular removal function, an eccentric rotation system is introduced to improve the LWE system. By controlling the eccentricity, it can achieve varied shapes removal function. When the rotary axis is controlled to a proper eccentricity, the removal function can be close to the Gaussian function. Moreover, the theoretical calculation and experimental validation are coincident and can give the research a steady foundation. The improvement not only can increase the adjustability of the removal function in LWE, but also can expand its applied field and provide reference for other ultra precision machining methods whose removal function does not have circular symmetry.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
504-509
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
June 2012
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: