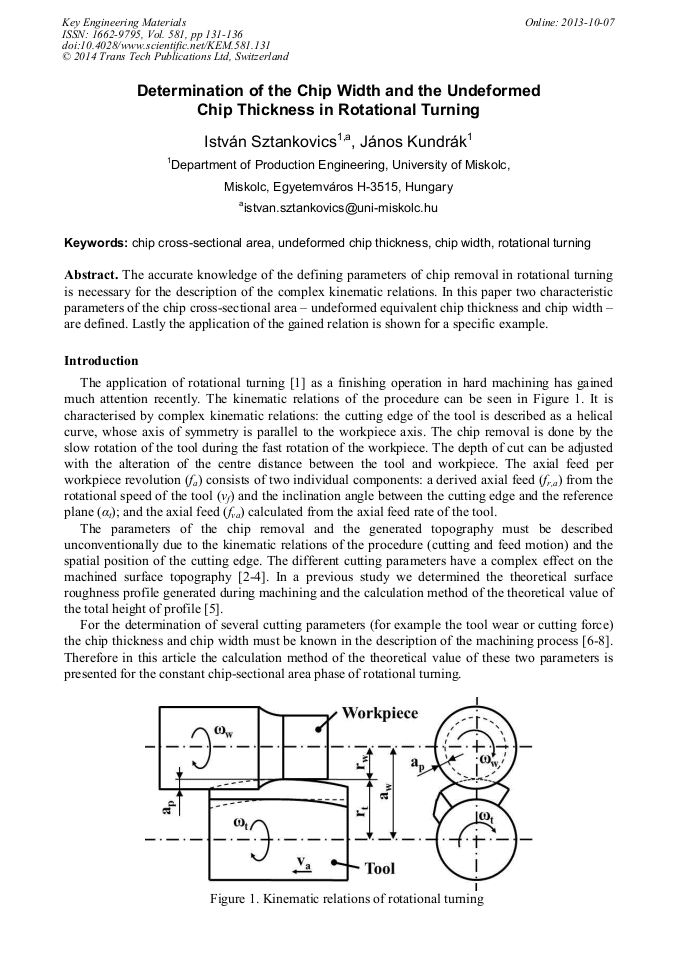
[1]
J.G. Weisser Söhne GmbH & Co: Patent Anmeldung, St. Georgen, Swartzwald, Germany, (2004).
Google Scholar
[2]
Mikó B, Beño J, Mañková I: Experimental Verification of Cusp Heights when 3D Milling Rounded Surfaces. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica (ISSN: 1785-8860), Vol. 9, No. 6, pp.101-116, (2012).
DOI: 10.12700/aph.9.6.2012.6.7
Google Scholar
[3]
Aykut S, Kentli A, Gülmez S: Robust Multiobjective Optimization of Cutting Parameters in Face Milling. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica (ISSN: 1785-8860), Vol. 9, No. 4, pp.85-100, (2012).
Google Scholar
[4]
Szabó O: Development of Ultraprecisional Turning. Proceedings of the Joint Hungarian - British International Mechatronics Conference, Budapest, Hungary, pp.121-126, (1994).
Google Scholar
[5]
Sztankovics I, Kundrák J: Theoretical Value of Total Height of Profile in Rotational Turning, Applied Mechanics and Materials (ISSN: 1662-7482), Vol. 309 (3rd Central European Conference on Logistics), pp.154-161, (2013).
DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.309.154
Google Scholar
[6]
Kundrak J: The Scientific Principles of Increasing the Effectiveness of Inner Surfaces' Cutting with CBN Tools. Academic Doctoral Dissertation. Kharkov, 368 p., (In Russian), (1996).
Google Scholar
[7]
Kountanya R, Al-Zkeri I, Altan T: Effect of tool edge geometry and cutting conditions on experimental and simulated chip morphology in orthogonal hard turning of 100Cr6 steel. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 209, pp.5068-5076, (2009).
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2009.02.011
Google Scholar
[8]
Čilková M, Neslušan M, Mičietová A, Mrázik J: Study of deformation processes after hard turning through acoustic emission, Manufacturing Technology (ISSN: 1213-2489), Vol. 12, No. 12, pp.13-17, (2012).
DOI: 10.21062/ujep/x.2012/a/1213-2489/mt/12/1/13
Google Scholar
[9]
Tschätsch H, Dietrich J: Praxis der Zerspantechnik, 10. Auflage, Vieweg+ Teubner Verlag, Wiesbaden, 393 p., (2011).
Google Scholar
[10]
Shaw M C: Metal Cutting Principles, Oxford University P, New York, 651 p., (2005).
Google Scholar
[11]
Sztankovics I, Kundrák J: Mathematical Description of Machining External Cylindrical Surface in Case of Rotational Turning, Cutting & Tooling in Technological System (ISSN 2078-7405), Kharkiv, Vol. 82, pp.264-269, (2012).
Google Scholar
[12]
Balajti Zs: Practical Application of the Monge Projection in the Production Process, microCAD 2010, International Scientific Conference, Section N: Production Engineering and Manufacturing Systems, Miskolc, 18-20 March 2010, pp.: 1-6.
Google Scholar