p.15
p.20
p.28
p.38
p.44
p.55
p.68
p.75
p.85
Influence of Oxygen on the Fatigue Behaviour of Ti-6Al-7Nb Alloy
Abstract:
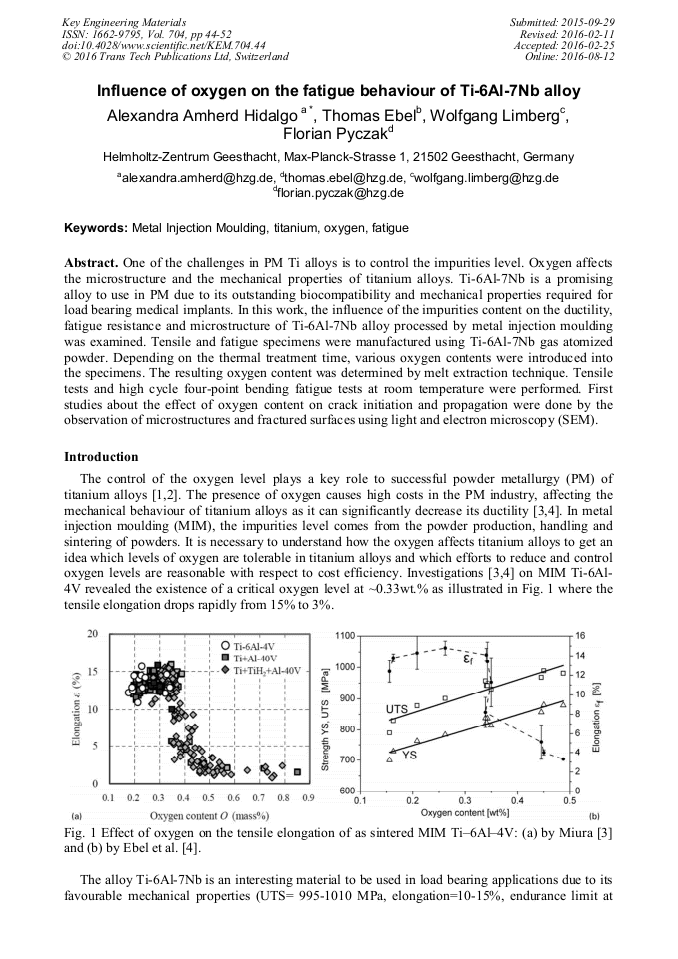
One of the challenges in PM Ti alloys is to control the impurities level. Oxygen affects the microstructure and the mechanical properties of titanium alloys. Ti-6Al-7Nb is a promising alloy to use in PM due to its outstanding biocompatibility and mechanical properties required for load bearing medical implants. In this work, the influence of the impurities content on the ductility, fatigue resistance and microstructure of Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy processed by metal injection moulding was examined. Tensile and fatigue specimens were manufactured using Ti-6Al-7Nb gas atomized powder. Depending on the thermal treatment time, various oxygen contents were introduced into the specimens. The resulting oxygen content was determined by melt extraction technique. Tensile tests and high cycle four-point bending fatigue tests at room temperature were performed. First studies about the effect of oxygen content on crack initiation and propagation were done by the observation of microstructures and fractured surfaces using light and electron microscopy (SEM).
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
44-52
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
August 2016
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2016 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: