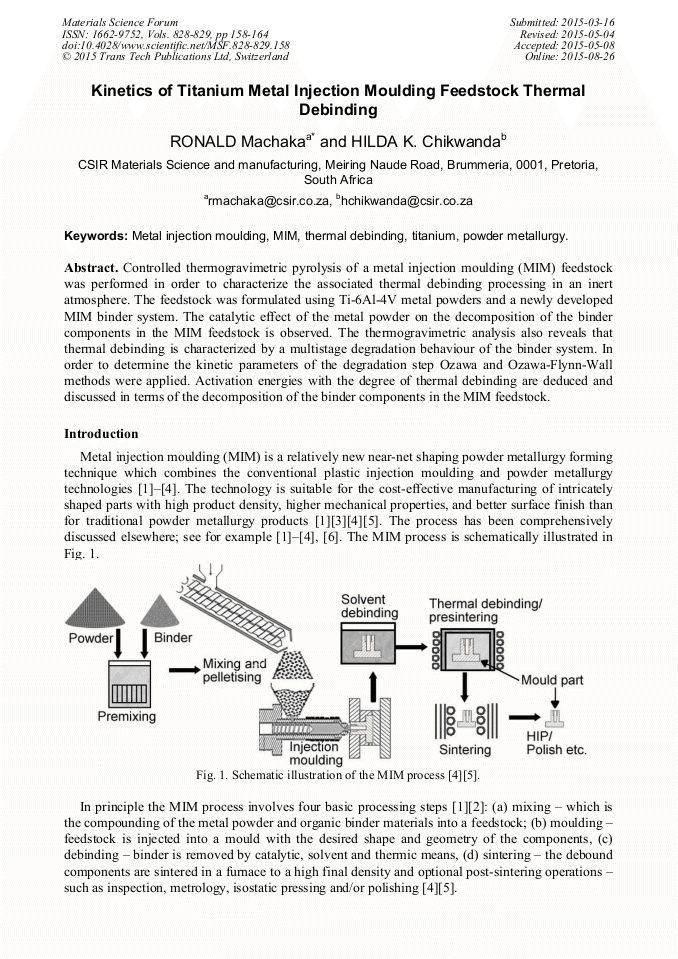
[1]
R. M. German, Progress in Titanium Metal Powder Injection Molding, Materials (Basel). 6(8) (2013) 3614–3662.
Google Scholar
[2]
G. Wen, P. Cao, B. Gabbitas, D. Zhang, and N. Edmonds, Development and Design of Binder Systems for Titanium Metal Injection Molding: An Overview, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 44(3) (2013) 1530–1547.
DOI: 10.1007/s11661-012-1485-x
Google Scholar
[3]
H. Ye, X. Y. Liu, and H. Hong, Fabrication of metal matrix composites by metal injection molding—A review, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 200(1–3) (2008) 12–24.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.10.066
Google Scholar
[4]
A. Sidambe, Biocompatibility of Advanced Manufactured Titanium Implants—A Review, Materials (Basel) 7(12) 2014 8168–8188.
DOI: 10.3390/ma7128168
Google Scholar
[5]
A. T. Sidambe, F. Derguti, and I. Todd, Metal Injection Moulding of Low Interstitial Titanium, Key Engineering Materials 520 (2012) 145–152.
DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.520.145
Google Scholar
[6]
M. Porter, Effects of Binder Systems for Metal Injection Moulding, Lulea University of Technology, (2003).
Google Scholar
[7]
Y. Li, L. Li, and K. A. Khalil, Effect of powder loading on metal injection molding stainless steels, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 183(2–3) (2007) 432–439.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.10.039
Google Scholar
[8]
R. Machaka, M. N. Seerane, and H. K. Chikwanda, Binder Development for Metal Injection Molding: A CSIR Perspective, Adv. Powder Metall. Part. Mater. 2014 (2014) 4–43.
Google Scholar
[9]
G. Aggarwal, S. J. Park, I. Smid, and R. M. German, Master decomposition curve for binders used in powder injection molding, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 38(3) (2007) 606–614.
DOI: 10.1007/s11661-007-9102-0
Google Scholar
[10]
C. B. DiAntonio, K. G. Ewsuk, and D. Bencoe, Extension of master sintering curve theory to organic decomposition, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88(10) (2005) 2722–2728.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2005.00517.x
Google Scholar
[11]
S. Das, Study of decomposition behaviour of binders and the effect of binder type on strength and density of alumina samples, BTech Thesis, Department of Ceramic Engineering, National Institute of Technology Rourkela, (2011).
Google Scholar
[12]
M. N. Seerane, H. K. Chikwanda, W. Focke, and R. Machaka, Investigating the Powder loading of gas atomised Ti6Al4V powder using an in-house, binder for MIM, in Advanced Metals Initiative: Precious Metals 2013, (2013).
Google Scholar
[13]
J. H. Flynn and L. A. Wall, A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data, J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Lett. 4(5) (1966) 323–328.
DOI: 10.1002/pol.1966.110040504
Google Scholar
[14]
T. Ozawa, Thermal analysis - Review and prospect, Thermochimica Acta 355(1–2) (2000) 35–42.
DOI: 10.1016/s0040-6031(00)00435-4
Google Scholar
[15]
J. Hidalgo, J. P. Fernández-Blázquez, A. Jiménez-Morales, T. Barriere, J. C. Gelin, and J. M. Torralba, Effect of the particle size and solids volume fraction on the thermal degradation behaviour of Invar 36 feedstocks, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 98(12) (2013).
DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.09.015
Google Scholar