p.3
p.11
p.17
p.22
p.28
p.35
p.41
p.46
p.52
Electronic Structure and Magnetic Properties of Iron Doped TiO2 (Rutile): XPS Measurements and CPA Calculations
Abstract:
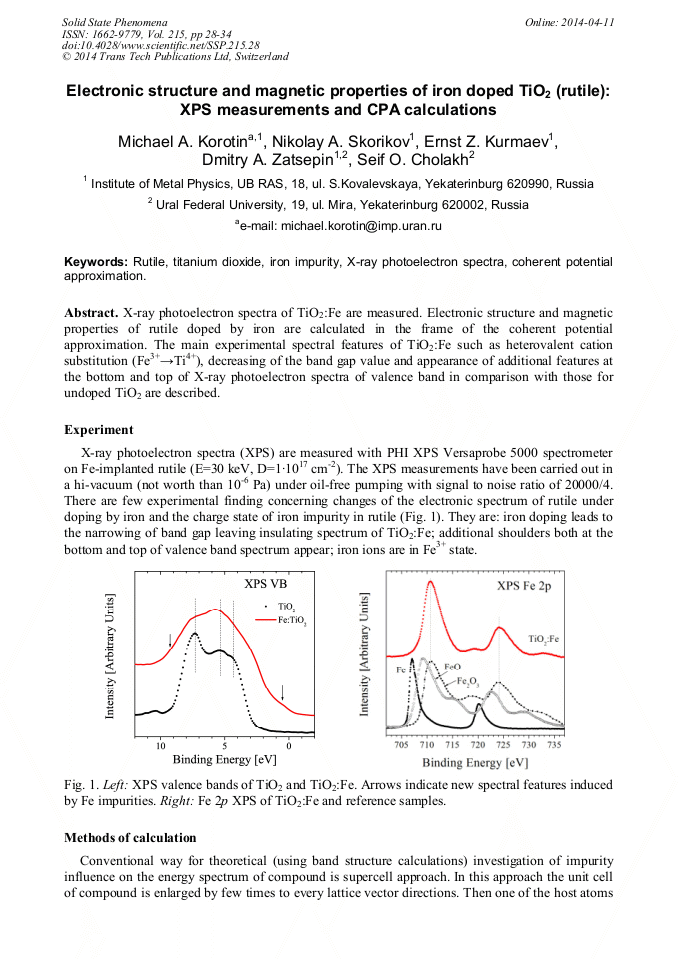
X-ray photoelectron spectra of TiO2:Fe are measured. Electronic structure and magnetic properties of rutile doped by iron are calculated in frames of the coherent potential approximation. The main experimental spectral features of TiO2:Fe such as heterovalent cation substitution (Fe3+→Ti4+), decreasing of the band gap value and appearance of additional features at the bottom and top of X-ray photoelectron spectra of valence band in comparison with those for undoped TiO2 are described.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
28-34
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
April 2014
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: