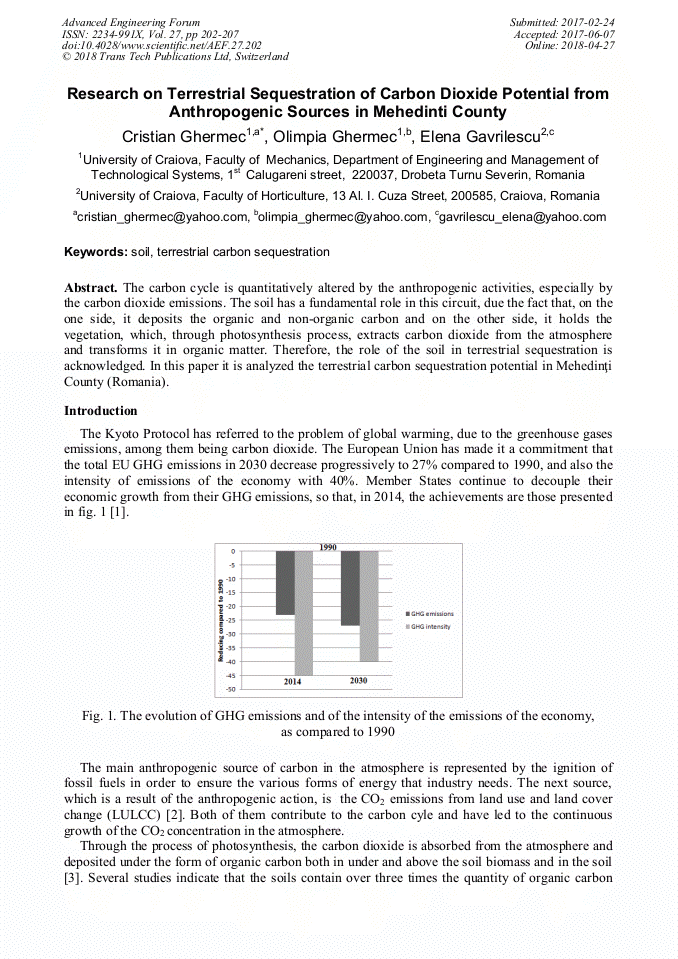
[1]
European Commission, COM(2015).
Google Scholar
[2]
J. P.W. Scharlemann, E.V.J. Tanner, R. Hiederer, V. Kapos, Global soil carbon: understanding and managing the largest terrestrial carbon pool, Carbon Management, 5:1(2014) 81-91.
DOI: 10.4155/cmt.13.77
Google Scholar
[3]
National Forest Administration - Romsilva, Monitoring plan for changes in carbon stocks in forest plantations (Afforestation of degraded agricultural land project in Romania) (2003), https://ji.unfccc.int/.../5MAHI24GUQ9WK6NXDPZSY1VE807OFT.
Google Scholar
[4]
B. Alemu, The Role of Forest and Soil Carbon Sequestrations on Climate Change Mitigation, Journal of Environment and Earth Science, (2014) 4(13): 98-111.
Google Scholar
[5]
M. Crossland, The carbon sequestration potential of hedges managed for woodfuel, The Organic Research Centre (2015).
Google Scholar
[6]
European Commission, COM(2016).
Google Scholar
[7]
F. B. Metting, G. K. Jacobs, J. S. Amthor, R. Dahlman, Terrestrial Carbon Sequestration Potential, Fuel Chem Div Prepr (2002) 47:5–6.
Google Scholar
[8]
R. Lal, Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security, Soils -the f inal f rontier, Science 304 (2004).
DOI: 10.1126/science.1097396
Google Scholar
[9]
Ministry of Environment and Forests, The National Romanian Strategy regarding Climatic Changes, The Official Gazette of Romania (2012), Part I, 536.
Google Scholar
[10]
http://www.meteoromania.ro/anm.
Google Scholar
[11]
L. Carlier, I. Rotar , R. Vidican, c Fixation of carbon dioxide: favorable for crop production and the environment, ProEnvironment 2 (2009) 73 –83, www.proenvironment.ro.
Google Scholar
[12]
National Forest Administration - Romsilva, Silvic Department of Mehedinţi, Report regarding the activity of the Silvic Department of Mehedinţi in (2015).
Google Scholar
[13]
M. Robert, Soil carbon sequestration for improved land management, http://www.fao.org/3/a-bl001e.pdf.
Google Scholar