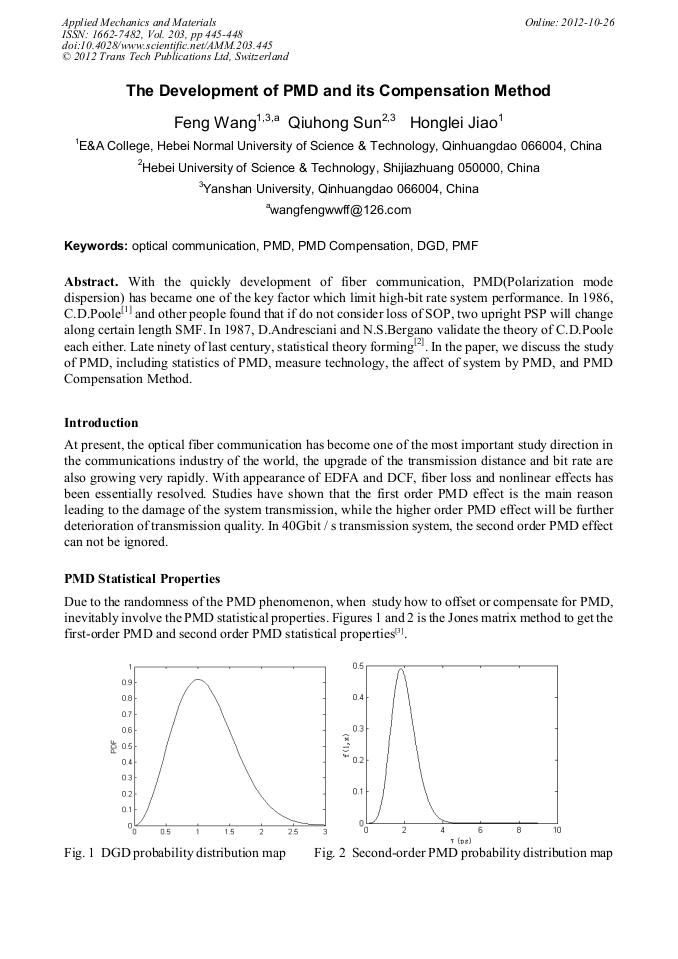
[1]
C.D. Poole, R E Wanger. Phenomenological approach to polarization dispersion in long single fibers. Electronic. Lett, 1986, 22(19), pp.1029-1030.
Google Scholar
[2]
Xing Wenlie, Wang Lindou, etal. Polarization mode dispersion management technique in high-speed optical communication systems. Optical Communication Technology. 2003, (6), pp.42-44.
Google Scholar
[3]
Zheng Yuan, Liu Yumin, etal. Study of the Statistical Characteristics of Second-order Polarization Mode Dispersion by Jones Transfer Matrix Method. Chinese Journal of Lasers. Vol. 1 (2003). pp.45-48.
Google Scholar
[4]
S. G. Evangelides, L. F. Mollenauer, J. P. Gordon et al. Polarization Multiplexing with soliton. JLightwave. Technol. Vol. 10 (1992). pp.28-35.
DOI: 10.1109/50.108732
Google Scholar
[5]
L. E. Nelson, R M. Jopson, and H. Kogelnik. Polarization Mode Dispersion Penalties Associated with Rotation of Principal States of Polarization in Optical Fiber, OFC2000, ThB2-1.
DOI: 10.1109/ofc.2000.868511
Google Scholar
[6]
H. Sunnerud, M. Karlsson and P. A. Andrekson. A comparison between NRZ and RZ data formats with respect to PMD-induced system degradation, OFC2000, W73-1.
DOI: 10.1364/ofc.2001.wt3
Google Scholar
[7]
C. Xie, M. Karlsson, P. A. Anderson, et al. Robustness of Dispersion-managed solitons to the polarization-mode dispersion in optical fibers, IEEE Photon. Technol. Left., Vol. 13 (2001), p. l21-123.
DOI: 10.1109/68.910508
Google Scholar
[8]
S. Lanne, D. Penninckx, J. P. Thiery, et al. Impact on chirping on polarization dispersion compensated systems. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. Vol. 12 (2000), pp.1492-1494.
DOI: 10.1109/68.887709
Google Scholar
[9]
H. F. Haunstein and H. M. Kalert. Influence of PMD on the performance of optical transmission systems in the presence of PDL. OFC2001, WT4-1.
Google Scholar
[10]
H. Sunnerud, J. Hansryd, P. A. Andrekson and M. Karlsson. Impact of PMD on FWM crosstalk in WDM Systems. OFC2000, ThB5-1.
DOI: 10.1109/ofc.2000.868514
Google Scholar
[11]
Winters J H. Experimental Equalization of Polarization Dispersion. Photon. Technol. Lett, Vol. 2 (1990). pp.591-593.
DOI: 10.1109/68.58058
Google Scholar
[12]
Hakki B W. Polarization Mode Dispersion Compensation by Phase Diversity Detection. Photon. Technol. Lett, Vol. 9 (1997). pp.121-123.
DOI: 10.1109/68.554528
Google Scholar
[13]
T. Ono,S. Yamazaki, H. Shimizu. Polarization control method for suppressing polarization in optical transmission systems. J. Lightwave Thchnology, Vol. 5 (1994), pp.891-898.
DOI: 10.1109/50.293983
Google Scholar
[14]
T. Takahashi, T. Imai, M. Aiki. Automatic compensation technique for timewise fluctuation polarization mode dispertion mode dispersion in in-line amplifier systems. Electronics Letters. Vol. 22 (1994), pp.348-349.
DOI: 10.1049/el:19940248
Google Scholar