p.273
p.278
p.283
p.289
p.297
p.302
p.315
p.321
p.326
A New Method to Control and Monitor a 6 D.O.F. Robot Arm
Abstract:
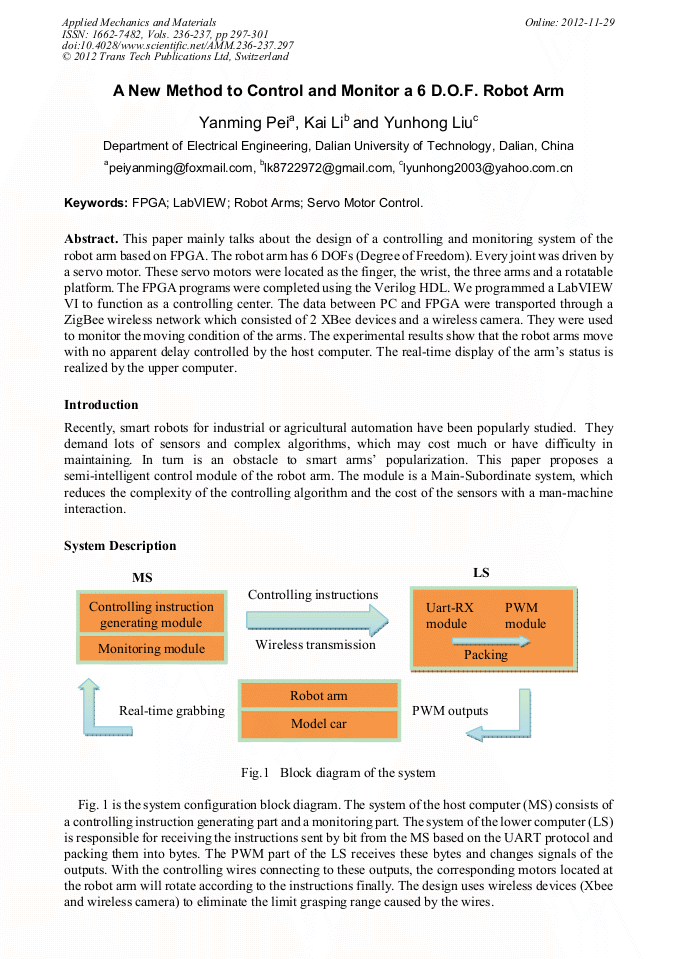
This paper mainly talks about the design of a controlling and monitoring system of the robot arm based on FPGA. The robot arm has 6 DOFs (Degree of Freedom). Every joint was driven by a servo motor. These servo motors were located as the finger, the wrist, the three arms and a rotatable platform. The FPGA programs were completed using the Verilog HDL. We programmed a LabVIEW VI to function as a controlling center. The data between PC and FPGA were transported through a ZigBee wireless network which consisted of 2 XBee devices and a wireless camera. They were used to monitor the moving condition of the arms. The experimental results show that the robot arms move with no apparent delay controlled by the host computer. The real-time display of the arm’s status is realized by the upper computer.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
297-301
Citation:
Online since:
November 2012
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: