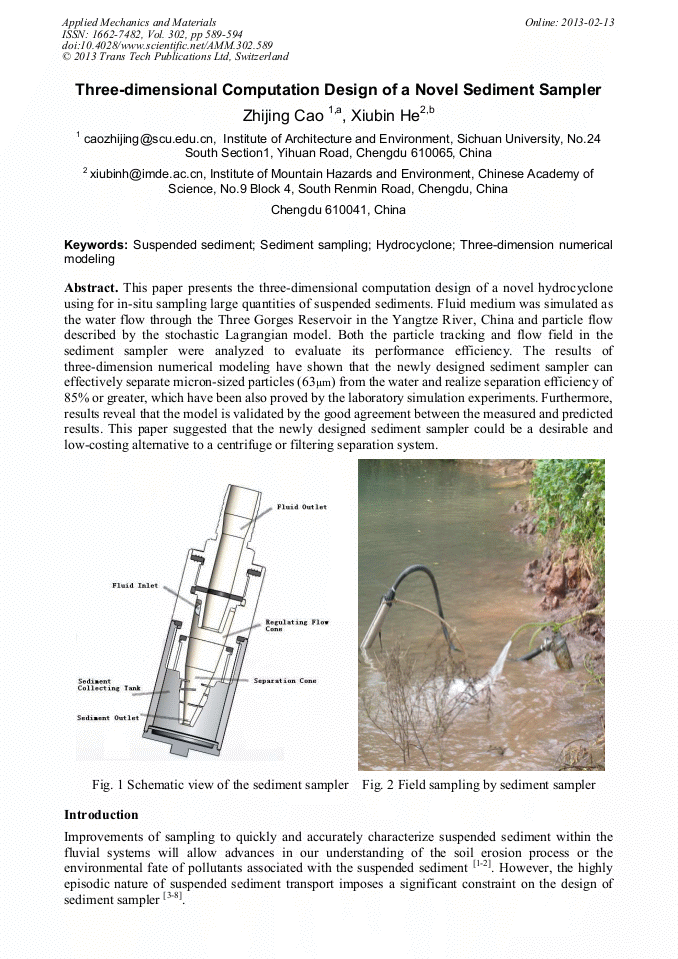
[1]
J.M. Phillips, M.A. Russel, D.E. Walling, Time-integrated sampling of fluvial suspended sediment: a simple methodology for small catchments, Hydro. Process. 14(2000)2589-2602.
DOI: 10.1002/1099-1085(20001015)14:14<2589::aid-hyp94>3.0.co;2-d
Google Scholar
[2]
Z.J. Cao, X.B. Zhang, N.S. Ai, Effect of sediment on concentration of dissolved phosphorus in the Three Gorges Reservoir, Int. J. Sediment Res. 26(2011)87-95.
DOI: 10.1016/s1001-6279(11)60078-4
Google Scholar
[3]
L.A. Bartsch, R.G. Rada, J.F. Sullivan, A comparison of solids collected in sediment traps and automated water sampler, Hydrobiologia. 323(1996)61-66.
DOI: 10.1007/bf00020547
Google Scholar
[4]
D.M. Hicks, M.J. Duncan, The efficiency of depth-integrating samplers in sampling the suspended sand load in gravel bed rivers, J. Hydrol. 201(1997)138-160.
DOI: 10.1016/s0022-1694(97)00040-1
Google Scholar
[5]
H.S. Herbert, G.A. Lutz, Collapsible-Bag Suspended-Sediment Sampler, J. Hydr. Eng. Dive- Asce. 106(1980)611-616.
DOI: 10.1061/jyceaj.0005409
Google Scholar
[6]
P.H. Jacobs, A new rechargeable dialysis pore water sampler for monitoring sub-aqueous in-situ sediment caps, Water Res. 36(2002)3121-3129.
DOI: 10.1016/s0043-1354(01)00542-5
Google Scholar
[7]
T. Schulze, M. Ricking, C. Schroter-Kermani, et al., The German Environmental Specimen Bank - Sampling, processing, and archiving sediment and suspended particulate matter, J. Soil Sediment. 7(2007)361-367.
DOI: 10.1065/jss2007.08.248
Google Scholar
[8]
W.R. Selbig, A. Cox, R.T. Bannerman, Verification of a depth-integrated sample arm as a means to reduce solids stratification bias in urban stormwater sampling, J. Environ. Monitor. 14(2012)1138-1144.
DOI: 10.1039/c2em10999a
Google Scholar
[9]
H.P. Pandit, N.M. Shakya, H. Stole, N.K. Garg, Hydraulic and sediment removal performance of a modified hydrocyclone, Miner. Eng. 22(2009)412-414.
DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2008.09.005
Google Scholar
[10]
B. Wang, K.W. Chu, A.B. Yu, A. Vince, Numerical studies of the effects of medium properties in dense medium cyclone operations, Miner. Eng. 22(2009)931-943.
DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2009.03.019
Google Scholar
[11]
P. Bagdi, J. P. Bhardwa, A.K. Sen, Analysis and simulation of a micro hydrocyclone device for particle liquid separation, Lab Chip. 11(2001)4012-4021.
DOI: 10.1039/c1lc20606k
Google Scholar
[12]
V.L. Streeter, E.B. Wylie, K.W. Bedford, Fluid Mechanics (Ninth Edition), Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, 2003, pp.105-210.
Google Scholar
[13]
M. Sommerfeld, Validation of a stochastic Lagrangian modeling approach for inter-particle collision in homogeneous isotropic turbulence, Int. J. Multiphas. Flow. 27(2001)1829-1858.
DOI: 10.1016/s0301-9322(01)00035-0
Google Scholar
[14]
B. Oesterlé, A. Petitjean, Simulations of particle-to-particle interactions in gas-solid flows, Int. J. Multiphas. Flow. 19(1993)199-211.
DOI: 10.1016/0301-9322(93)90033-q
Google Scholar
[15]
B. Wang, A.B. Yu, Computational investigation of the mechanisms of particle separation and fish-hook, phenomenon in hydrocyclones, Aiche. Journal. 56(2010)1703-1715.
DOI: 10.1002/aic.12114
Google Scholar
[16]
S. Heinrich, Which demands should and can meet a separation model for hydrocyclone classification? Int. J. Miner. Process. 96(2010)14-26.
DOI: 10.1016/j.minpro.2010.04.003
Google Scholar
[17]
A.F. Nowkowski, M.J. Doby, The numerical modelling of the flow in hydrocyclones, Kona. 26(2008)66-80.
DOI: 10.14356/kona.2008008
Google Scholar
[18]
J.A. Delgadillo, R.K. Rajamani, Exploration of hydrocyclone designs using computational fluid dynamics, Int. J. Miner. Process. 84(2007)252-261.
DOI: 10.1016/j.minpro.2006.07.014
Google Scholar