p.2404
p.2409
p.2414
p.2428
p.2433
p.2438
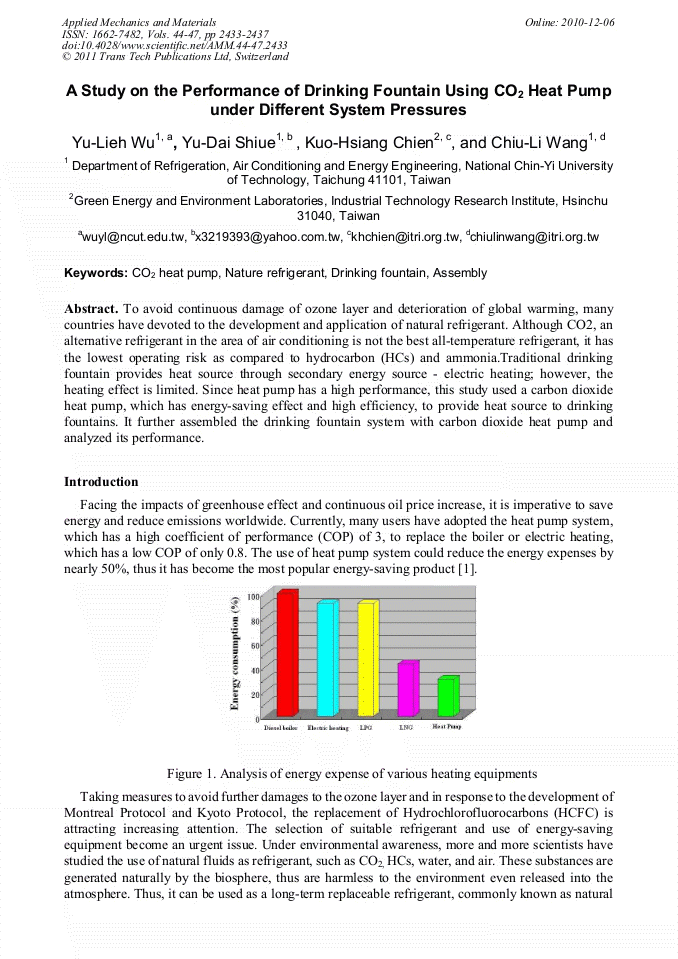
p.2443
p.2448
p.2453
A Study on the Performance of Drinking Fountain Using CO2 Heat Pump under Different System Pressures
Abstract:
To avoid continuous damage of ozone layer and deterioration of global warming, many countries have devoted to the development and application of natural refrigerant. Although CO2, an alternative refrigerant in the area of air conditioning is not the best all-temperature refrigerant, it has the lowest operating risk as compared to hydrocarbon (HCs) and ammonia.Traditional drinking fountain provides heat source through secondary energy source - electric heating; however, the heating effect is limited. Since heat pump has a high performance, this study used a carbon dioxide heat pump, which has energy-saving effect and high efficiency, to provide heat source to drinking fountains. It further assembled the drinking fountain system with carbon dioxide heat pump and analyzed its performance.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
2433-2437
Citation:
Online since:
December 2010
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: