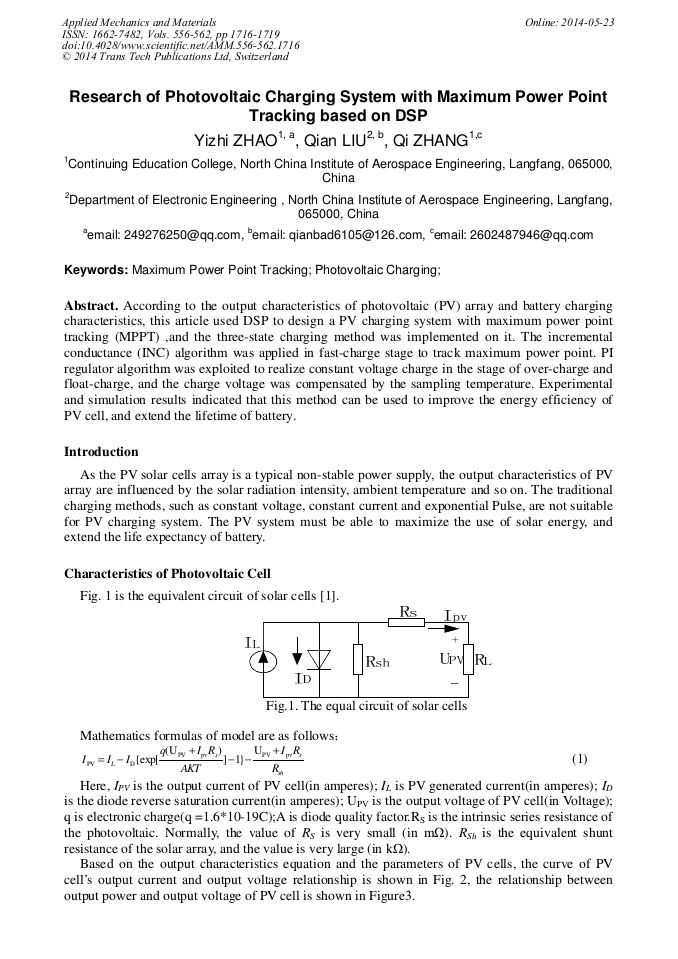
[1]
N. Mutoh, M. Ohno, and T. Inoue. A Control Method to Charge Series-Connected Ultra electric Double-Layer Capacitors Suitable for Photovoltaic Generate Systems Combining MPPT Control Method. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2007, vol. 54, no. 1, pp.374-383.
DOI: 10.1109/tie.2006.885149
Google Scholar
[2]
Sera, D., Teodorescu, R., Hatchel, J., Knoll, M. Optimized maximum power point tracker for fast-changing environmental conditions. 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, July 2008, p.2401~2407.
DOI: 10.1109/isie.2008.4677275
Google Scholar
[3]
Li Lianbing, Ma Qiang, Zhao Qingyun. Research of MPPT algorithm with stability and rapidity. 2008 Chinese Control and Decision Conference, July 2008, p.5210~5214.
DOI: 10.1109/ccdc.2008.4598324
Google Scholar
[4]
Fang Luo, Pengwei Xu, Yong Kang, Shangxu Duan. A variable step maximum power point tracking method using differential equation solution. 2nd IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, May 2007, p.2259~2263.
DOI: 10.1109/iciea.2007.4318813
Google Scholar
[5]
Hohm D.P. Ropp M.E. Comparative study of maximum power point tracking algorithms using an experimental, programmable, maximum power point tracking test bed. Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, 2000, Conference Record of the Twenty-Eight IEEE, 2000, pp.1699-1702.
DOI: 10.1109/pvsc.2000.916230
Google Scholar
[6]
Jun Pan, Chenghua Wang, Feng Hong. Research of Photovoltaic Charging System with Maximum Power Point Tracking. the Ninth International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments, 2009, p.478 ~481.
DOI: 10.1109/icemi.2009.5274013
Google Scholar
[7]
Masoum, M.A. S, Badejani, S.M.M., Fuchs, E.F. Microprocessor controlled new class of optimal battery chargers for photovoltaic applications. IEEE Transaction on Energy Conversion, June 2004, p.549~550.
DOI: 10.1109/pes.2004.1373118
Google Scholar
[8]
Colak, I., Tuncay, N. High current, low voltage modular power converter for lead acid battery charging. 2008 IEEE International Conference on Sustainable Energy Technologies, Nov 2008 p.1042~1046.
DOI: 10.1109/icset.2008.4747160
Google Scholar