p.1036
p.1041
p.1045
p.1049
p.1054
p.1059
p.1063
p.1068
p.1073
Multi-Robot Fish Path Planning Based on the Modified A* Algorithm
Abstract:
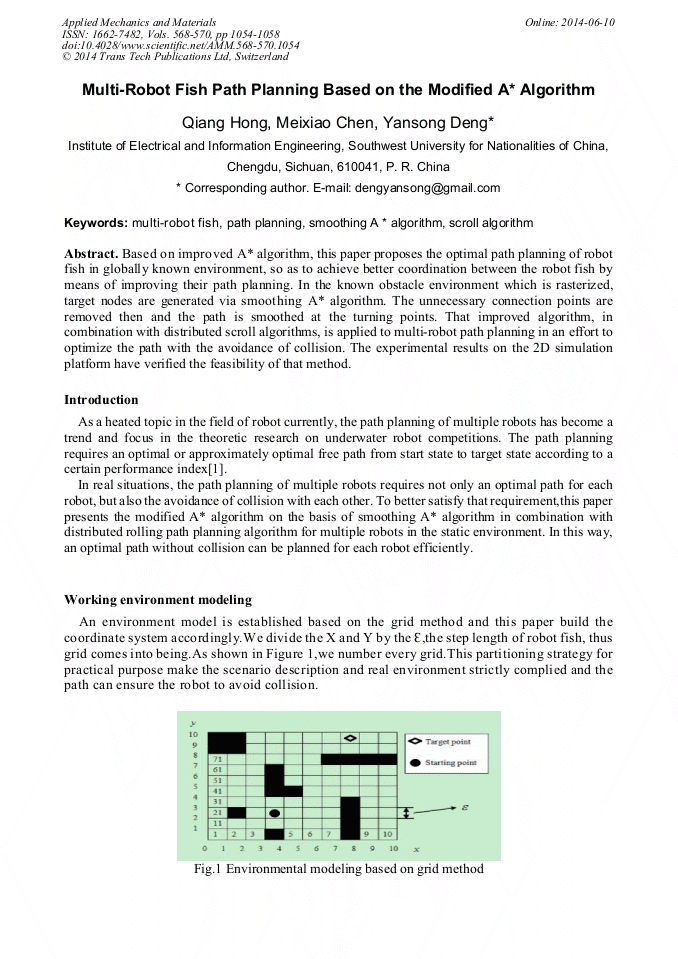
Based on improved A* algorithm, this paper proposes the optimal path planning of robot fish in globally known environment, so as to achieve better coordination between the robot fish by means of improving their path planning. In the known obstacle environment which is rasterized, target nodes are generated via smoothing A* algorithm. The unnecessary connection points are removed then and the path is smoothed at the turning points. That improved algorithm, in combination with distributed scroll algorithms, is applied to multi-robot path planning in an effort to optimize the path with the avoidance of collision. The experimental results on the 2D simulation platform have verified the feasibility of that method.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1054-1058
Citation:
Online since:
June 2014
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: