p.1199
p.1203
p.1207
p.1212
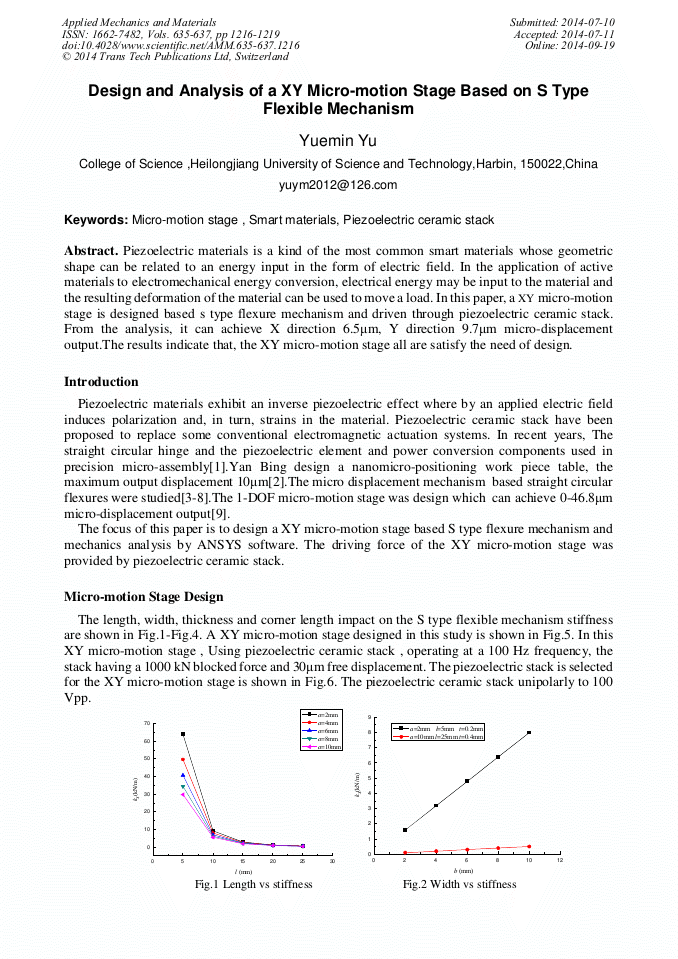
p.1216
p.1220
p.1224
p.1228
p.1232
Design and Analysis of a XY Micro-Motion Stage Based on S Type Flexible Mechanism
Abstract:
Piezoelectric materials is a kind of the most common smart materials whose geometric shape can be related to an energy input in the form of electric field. In the application of active materials to electromechanical energy conversion, electrical energy may be input to the material and the resulting deformation of the material can be used to move a load. In this paper, a XY micro-motion stage is designed based s type flexure mechanism and driven through piezoelectric ceramic stack. From the analysis, it can achieve X direction 6.5μm, Y direction 9.7μm micro-displacement output.The results indicate that, the XY micro-motion stage all are satisfy the need of design.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1216-1219
Citation:
Online since:
September 2014
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: