p.201
p.207
p.213
p.219
p.225
p.231
p.237
p.243
p.249
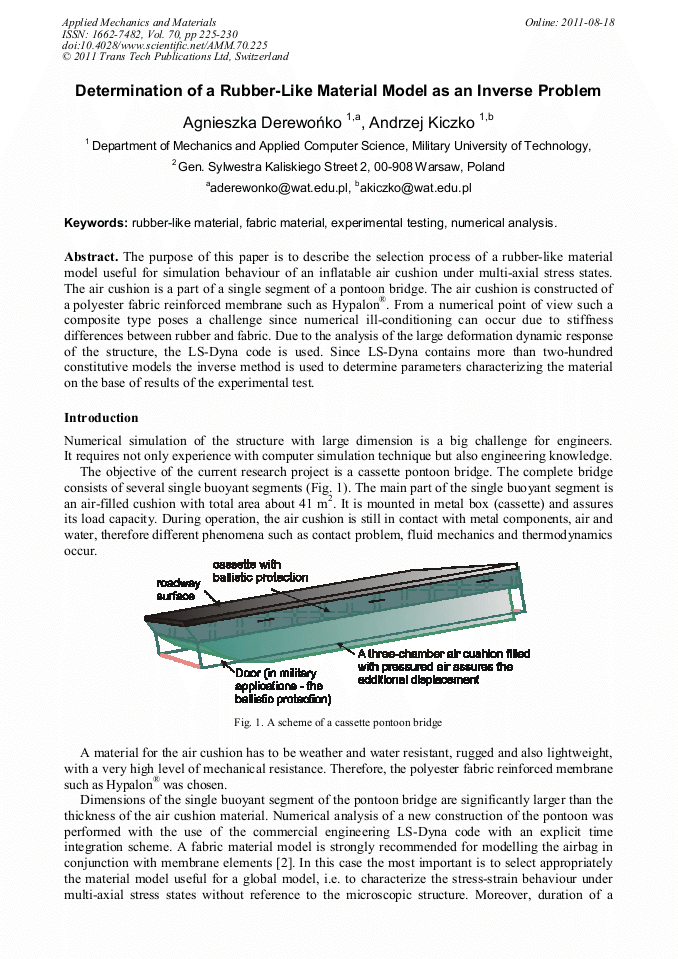
Determination of a Rubber-Like Material Model as an Inverse Problem
Abstract:
The purpose of this paper is to describe the selection process of a rubber-like material model useful for simulation behaviour of an inflatable air cushion under multi-axial stress states. The air cushion is a part of a single segment of a pontoon bridge. The air cushion is constructed of a polyester fabric reinforced membrane such as Hypalon®. From a numerical point of view such a composite type poses a challenge since numerical ill-conditioning can occur due to stiffness differences between rubber and fabric. Due to the analysis of the large deformation dynamic response of the structure, the LS-Dyna code is used. Since LS-Dyna contains more than two-hundred constitutive models the inverse method is used to determine parameters characterizing the material on the base of results of the experimental test.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
225-230
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
August 2011
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: