p.337
p.342
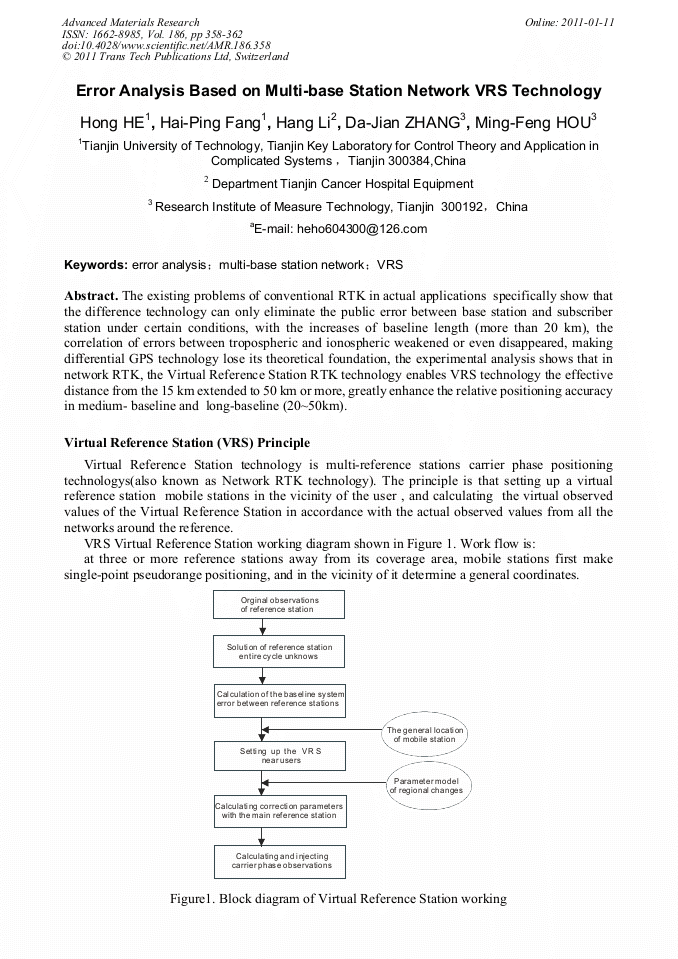
p.348
p.353
p.358
p.363
p.368
p.373
p.378
Error Analysis Based on Multi-Base Station Network VRS Technology
Abstract:
The existing problems of conventional RTK in actual applications specifically show that the difference technology can only eliminate the public error between base station and subscriber station under certain conditions, with the increases of baseline length (more than 20 km), the correlation of errors between tropospheric and ionospheric weakened or even disappeared, making differential GPS technology lose its theoretical foundation, the experimental analysis shows that in network RTK, the Virtual Reference Station RTK technology enables VRS technology the effective distance from the 15 km extended to 50 km or more, greatly enhance the relative positioning accuracy in medium- baseline and long-baseline (20~50km).
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
358-362
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
January 2011
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: