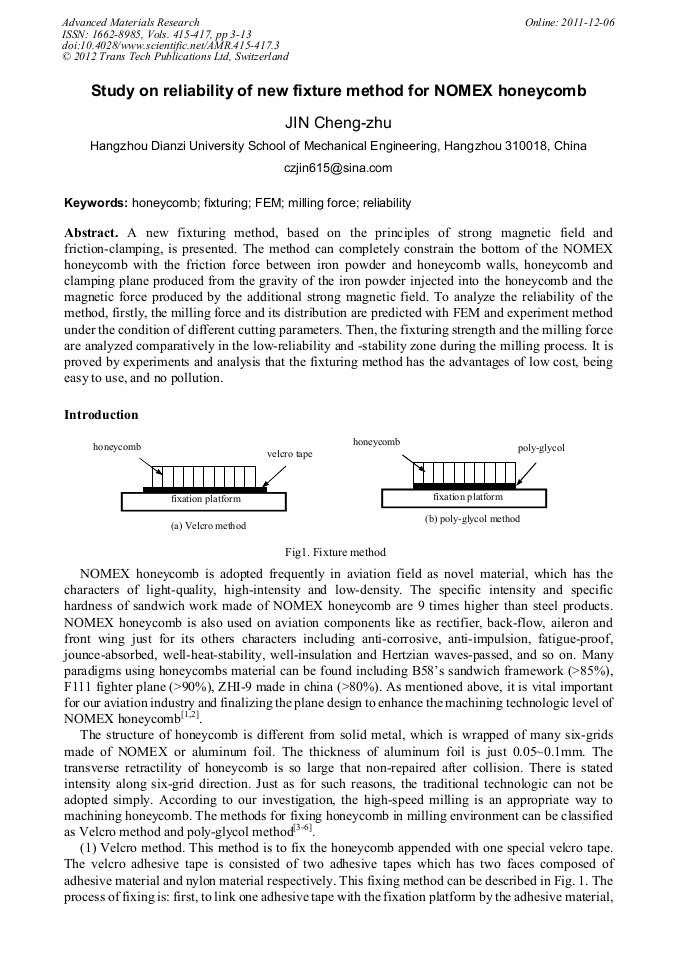
p.3
p.14
p.19
p.25
p.30
p.35
p.39
p.43
Study on Reliability of New Fixture Method for NOMEX Honeycomb
Abstract:
A new fixturing method, based on the principles of strong magnetic field and friction-clamping, is presented. The method can completely constrain the bottom of the NOMEX honeycomb with the friction force between iron powder and honeycomb walls, honeycomb and clamping plane produced from the gravity of the iron powder injected into the honeycomb and the magnetic force produced by the additional strong magnetic field. To analyze the reliability of the method, firstly, the milling force and its distribution are predicted with FEM and experiment method under the condition of different cutting parameters. Then, the fixturing strength and the milling force are analyzed comparatively in the low-reliability and -stability zone during the milling process. It is proved by experiments and analysis that the fixturing method has the advantages of low cost, being easy to use, and no pollution.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
3-13
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
December 2011
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: