p.59
p.63
p.67
p.71
p.75
p.80
p.84
p.88
p.92
Process Tomographic Measurements of Granular Flow in a Pneumatic Conveying System
Abstract:
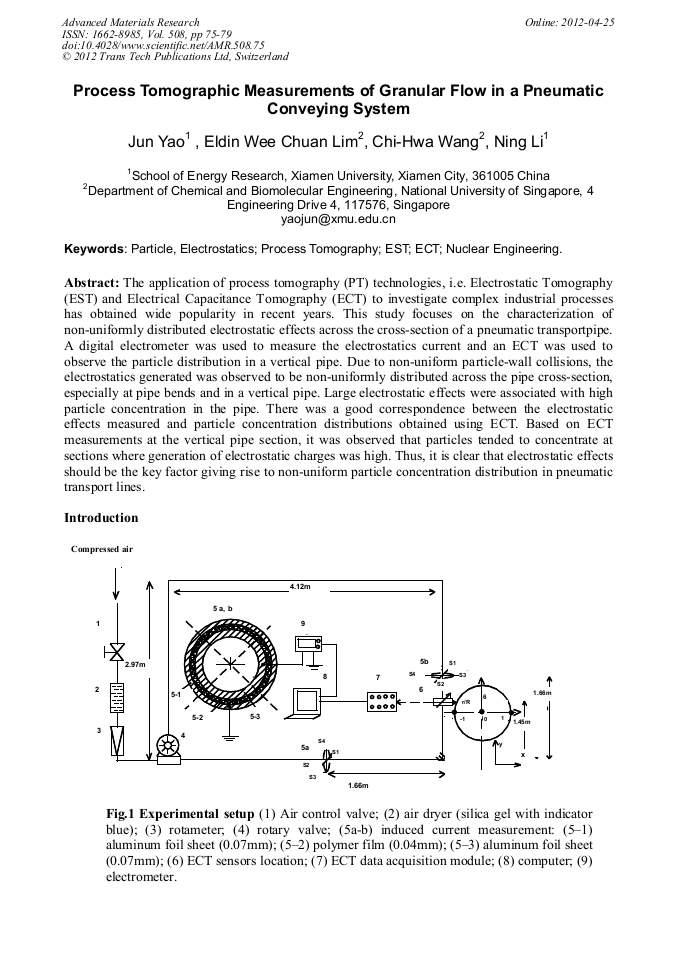
The application of process tomography (PT) technologies, i.e. Electrostatic Tomography (EST) and Electrical Capacitance Tomography (ECT) to investigate complex industrial processes has obtained wide popularity in recent years. This study focuses on the characterization of non-uniformly distributed electrostatic effects across the cross-section of a pneumatic transportpipe. A digital electrometer was used to measure the electrostatics current and an ECT was used to observe the particle distribution in a vertical pipe. Due to non-uniform particle-wall collisions, the electrostatics generated was observed to be non-uniformly distributed across the pipe cross-section, especially at pipe bends and in a vertical pipe. Large electrostatic effects were associated with high particle concentration in the pipe. There was a good correspondence between the electrostatic effects measured and particle concentration distributions obtained using ECT. Based on ECT measurements at the vertical pipe section, it was observed that particles tended to concentrate at sections where generation of electrostatic charges was high. Thus, it is clear that electrostatic effects should be the key factor giving rise to non-uniform particle concentration distribution in pneumatic transport lines.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
75-79
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
April 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: