p.822
p.826
p.830
p.834
p.839
p.843
p.847
p.851
p.856
A Low Temperature Coefficient, High Voltage Detection Circuit Used in Power over Ethernet
Abstract:
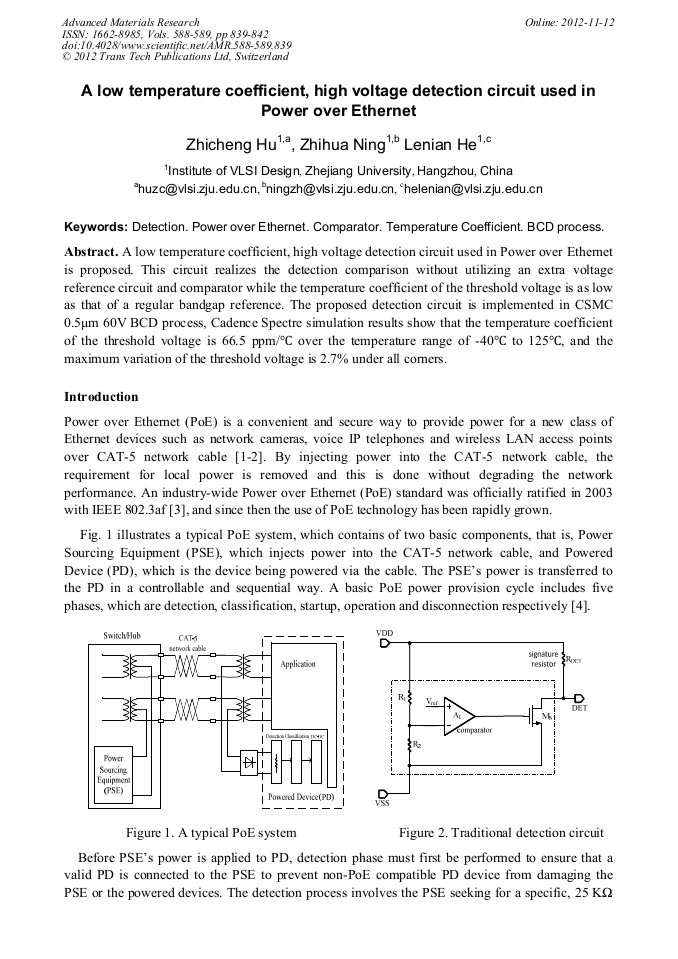
A low temperature coefficient, high voltage detection circuit used in Power over Ethernet is proposed. This circuit realizes the detection comparison without utilizing an extra voltage reference circuit and comparator while the temperature coefficient of the threshold voltage is as low as that of a regular bandgap reference. The proposed detection circuit is implemented in CSMC 0.5μm 60V BCD process, Cadence Spectre simulation results show that the temperature coefficient of the threshold voltage is 66.5 ppm/°C over the temperature range of -40°C to 125°C, and the maximum variation of the threshold voltage is 2.7% under all corners.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
839-842
Citation:
Online since:
November 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: