p.350
p.354
p.359
p.364
p.368
p.372
p.377
p.382
p.389
Effects of Mineral Admixtures and Superplasticizer on Controlling Hydration Heat of Cementitious Materials
Abstract:
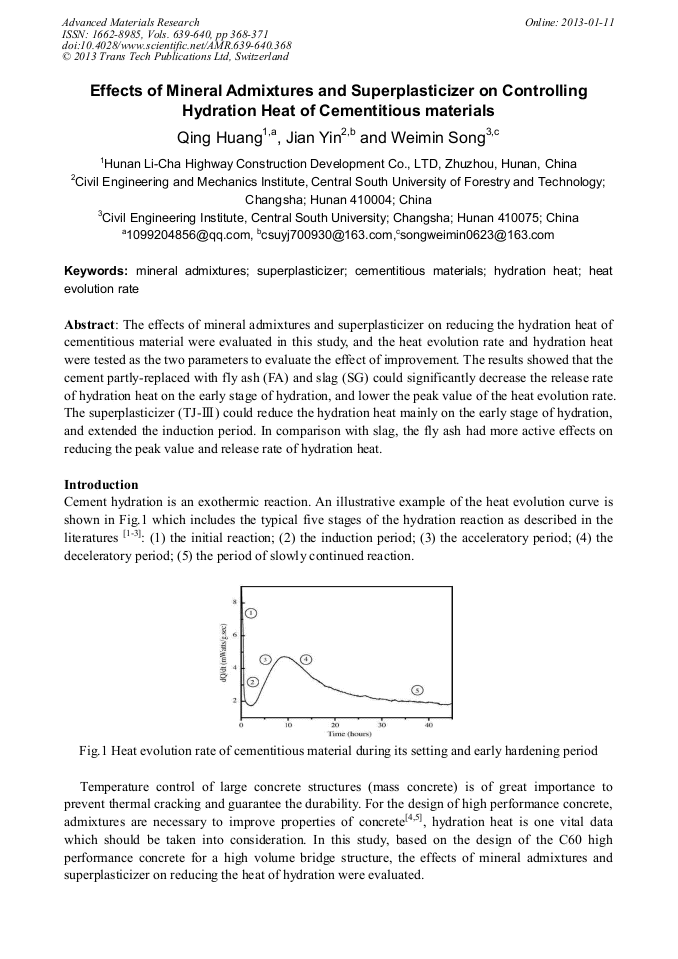
The effects of mineral admixtures and superplasticizer on reducing the hydration heat of cementitious material were evaluated in this study, and the heat evolution rate and hydration heat were tested as the two parameters to evaluate the effect of improvement. The results showed that the cement partly-replaced with fly ash (FA) and slag (SG) could significantly decrease the release rate of hydration heat on the early stage of hydration, and lower the peak value of the heat evolution rate. The superplasticizer (TJ-Ⅲ) could reduce the hydration heat mainly on the early stage of hydration, and extended the induction period. In comparison with slag, the fly ash had more active effects on reducing the peak value and release rate of hydration heat.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
368-371
Citation:
Online since:
January 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: