p.321
p.326
p.331
p.336
p.343
p.348
p.354
p.359
p.364
Analysis of Bursting Crack of Bottom Slab and Reinforcement for a Large Continuous Girder Bridge
Abstract:
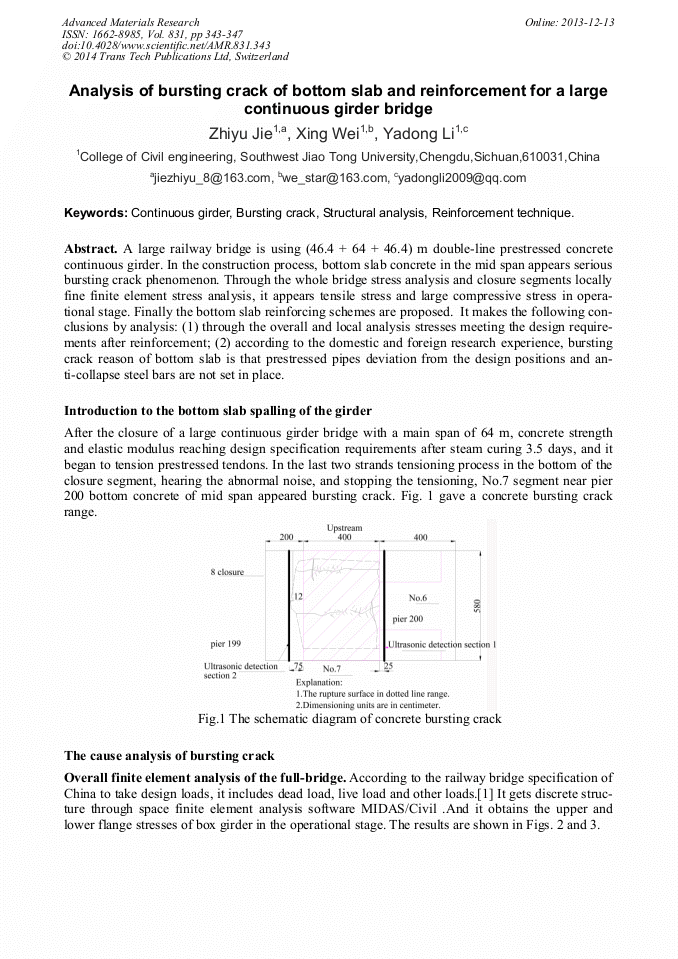
A large railway bridge is using (46.4 + 64 + 46.4) m double-line prestressed concrete continuous girder. In the construction process, bottom slab concrete in the mid span appears serious bursting crack phenomenon. Through the whole bridge stress analysis and closure segments locally fine finite element stress analysis, it appears tensile stress and large compressive stress in operational stage. Finally the bottom slab reinforcing schemes are proposed. It makes the following conclusions by analysis: (1) through the overall and local analysis stresses meeting the design requirements after reinforcement; (2) according to the domestic and foreign research experience, bursting crack reason of bottom slab is that prestressed pipes deviation from the design positions and anti-collapse steel bars are not set in place.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
343-347
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
December 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: