p.253
p.259
p.263
p.269
p.277
p.283
p.290
p.296
p.304
Design Optimization of an Industrial Muffler by Taguchi Method
Abstract:
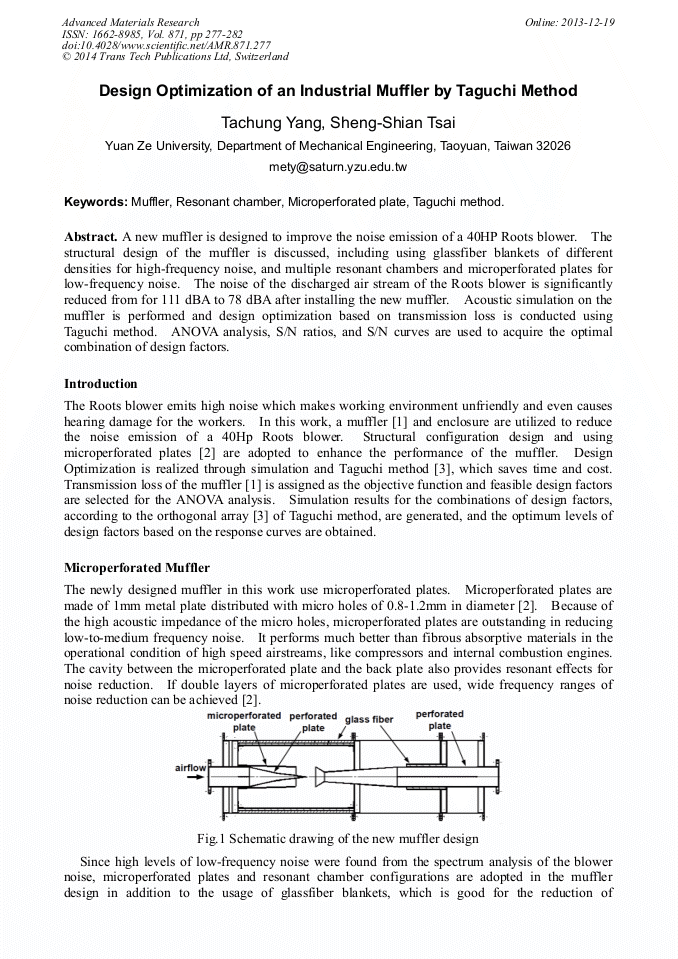
A new muffler is designed to improve the noise emission of a 40HP Roots blower. The structural design of the muffler is discussed, including using glassfiber blankets of different densities for high-frequency noise, and multiple resonant chambers and microperforated plates for low-frequency noise. The noise of the discharged air stream of the Roots blower is significantly reduced from for 111 dBA to 78 dBA after installing the new muffler. Acoustic simulation on the muffler is performed and design optimization based on transmission loss is conducted using Taguchi method. ANOVA analysis, S/N ratios, and S/N curves are used to acquire the optimal combination of design factors.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
277-282
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
December 2013
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: