p.242
p.246
p.251
p.257
p.261
p.265
p.270
p.275
p.280
Resolving National Energy Crisis through Energy Efficient Appliances: Use of Ground Water Heat Pump for Air Conditioning Systems
Abstract:
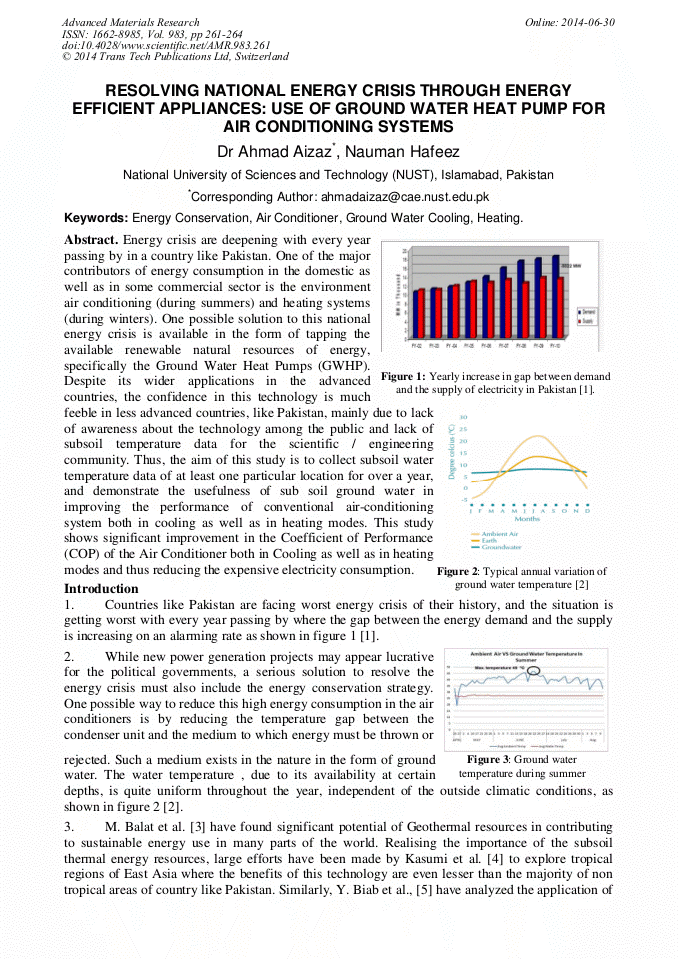
Energy crisis are deepening with every year passing by in a country like Pakistan. One of the major contributors of energy consumption in the domestic as well as in some commercial sector is the environment air conditioning (during summers) and heating systems (during winters). One possible solution to this national energy crisis is available in the form of tapping the available renewable natural resources of energy, specifically the Ground Water Heat Pumps (GWHP). Despite its wider applications in the advanced countries, the confidence in this technology is much feeble in less advanced countries, like Pakistan, mainly due to lack of awareness about the technology among the public and lack of subsoil temperature data for the scientific / engineering community. Thus, the aim of this study is to collect subsoil water temperature data of at least one particular location for over a year, and demonstrate the usefulness of sub soil ground water in improving the performance of conventional air-conditioning system both in cooling as well as in heating modes. This study shows significant improvement in the Coefficient of Performance (COP) of the Air Conditioner both in Cooling as well as in heating modes and thus reducing the expensive electricity consumption.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
261-264
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
June 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: