p.2128
p.2134
p.2140
p.2146
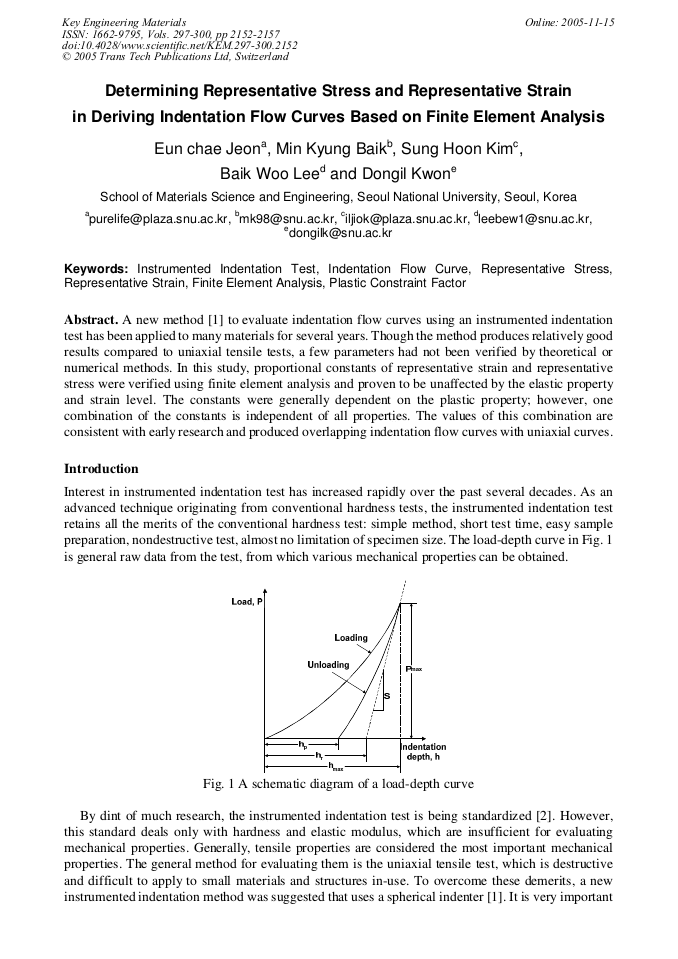
p.2152
p.2158
p.2164
p.2169
p.2176
Determining Representative Stress and Representative Strain in Deriving Indentation Flow Curves Based on Finite Element Analysis
Abstract:
A new method [1] to evaluate indentation flow curves using an instrumented indentation test has been applied to many materials for several years. Though the method produces relatively good results compared to uniaxial tensile tests, a few parameters had not been verified by theoretical or numerical methods. In this study, proportional constants of representative strain and representative stress were verified using finite element analysis and proven to be unaffected by the elastic property and strain level. The constants were generally dependent on the plastic property; however, one combination of the constants is independent of all properties. The values of this combination are consistent with early research and produced overlapping indentation flow curves with uniaxial curves.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
2152-2157
Citation:
Online since:
November 2005
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2005 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: