p.777
p.782
p.786
p.792
p.797
p.803
p.807
p.811
p.816
Stress Distribution Model between Lunar Rover Wheel-Leg Foot and Lunar Soil
Abstract:
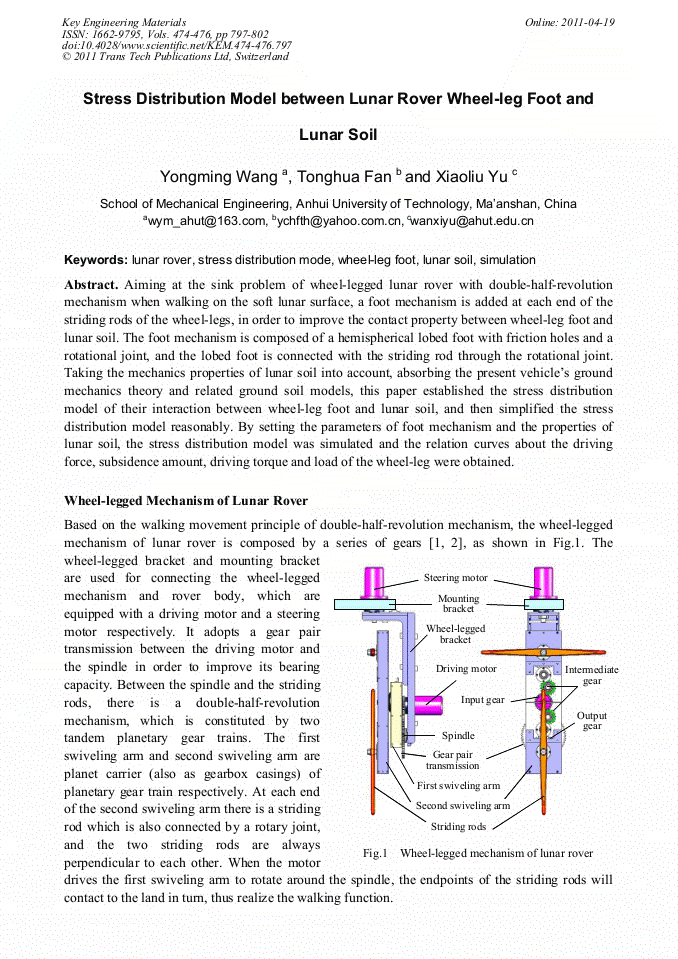
Aiming at the sink problem of wheel-legged lunar rover with double-half-revolution mechanism when walking on the soft lunar surface, a foot mechanism is added at each end of the striding rods of the wheel-legs, in order to improve the contact property between wheel-leg foot and lunar soil. The foot mechanism is composed of a hemispherical lobed foot with friction holes and a rotational joint, and the lobed foot is connected with the striding rod through the rotational joint. Taking the mechanics properties of lunar soil into account, absorbing the present vehicle’s ground mechanics theory and related ground soil models, this paper established the stress distribution model of their interaction between wheel-leg foot and lunar soil, and then simplified the stress distribution model reasonably. By setting the parameters of foot mechanism and the properties of lunar soil, the stress distribution model was simulated and the relation curves about the driving force, subsidence amount, driving torque and load of the wheel-leg were obtained.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
797-802
Citation:
Online since:
April 2011
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: