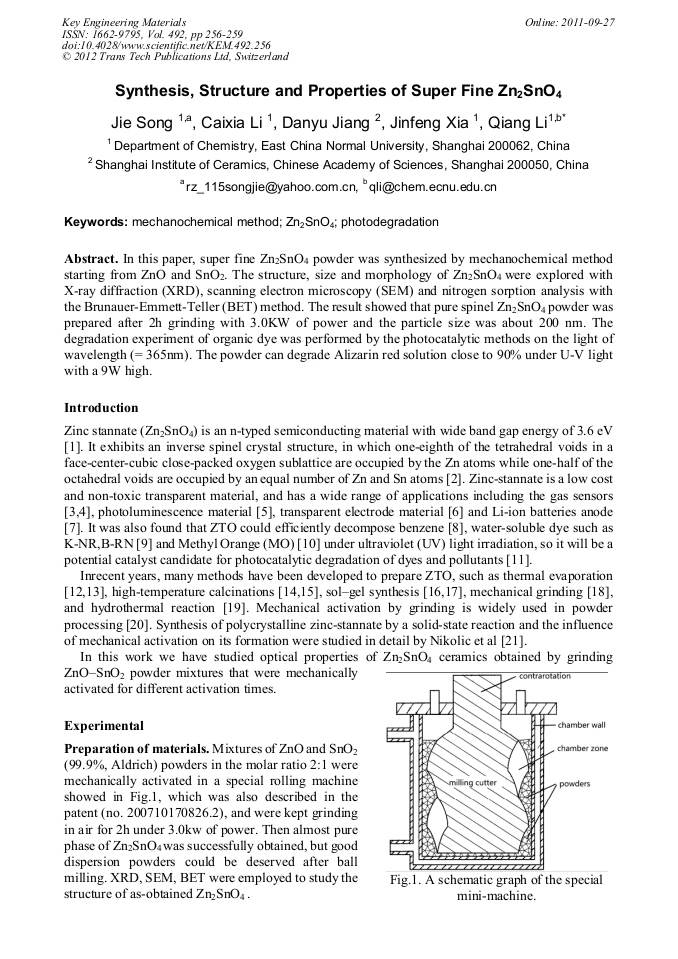
[1]
T. Minami, H. Sonohara, S. Takata, H. Sato: Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 Vol. 33 (1994), p. L1693.
Google Scholar
[2]
H.F. Lin, S.C. Liao, S.W. Hung, C.T. Hu: Mater. Chem. Phys. (2009).
Google Scholar
[3]
J.H. Yu, G.M. Choi: Sens. Actuators B Vol. 72 (2001), p.141.
Google Scholar
[4]
Y. Yamada, Y. Seno, Y. Masuka, K. Yamashita: Sens. Actuators B Vol. 49 (1998), p.248.
Google Scholar
[5]
J.X. Wang, S.S. Xie, H.J. Yuan, et al.: Solid State Commun. (2004), p.131.
Google Scholar
[6]
X.L. Fu, X.X. Wang, J.L. Long: J. Solid State Chem. Vol. 182 (2009), Vol. 517.
Google Scholar
[7]
F. Belliard, P.A. Connor, J.T.S. Irvine: Solid State Ionics Vol. 135 (2000), p.163.
Google Scholar
[8]
W.X. Cun, J.C. Zhao, B.X. Mai, et al.: J. Mater. Sci. Vol. 37 (2002), p.2898.
Google Scholar
[9]
X. Lou, X. Jia, J. Xu, et al.: Mater. Sci. Eng. A Vol. 432 (2006), p.221.
Google Scholar
[10]
S. Wang, Z. Yang, M. Lu, et al.: Mater. Lett. Vol. 61 (2007), p.3005.
Google Scholar
[11]
Y.X. Lin, S. Lin, M.H. Luo, J.H. Liu: Mater. Lett. Vol. 63 (2009), p.1169.
Google Scholar
[12]
H.Y. Chen, J.X. Wang, H.C. Yu, et al.: J. Phys. Chem. B Vol. 109 (2005), p.2573.
Google Scholar
[13]
J.S. Jie, G.Z. Wang, X.H. Han, et al.: J. Phys. Chem. B Vol. 108 (2004), p.8249.
Google Scholar
[14]
W. Cun, X.M. Wang, J.C. Zhao, et al.: J. Mater. Sci. Vol. 37 (2002), p.2989.
Google Scholar
[15]
M.L. Zhang, T.C. An, X.H. Hu, et al.: Appl. Catal. A Vol. 260 (2004), p.215.
Google Scholar
[16]
G. Fu, H. Chen, Z.X. Chen, et al.: Sens. Actuator B Vol. 81 (2002), p.308.
Google Scholar
[17]
A. Kurz, K. Brakecha, J. Puetz, M.A. Aegerter: Thin Solid Films Vol. 502 (2006), p.212.
DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2005.07.276
Google Scholar
[18]
N. Nikolic, Z. Marinkovic, T. Sreckovic: J. Mater. Sci. Vol. 39 (2004), p.5239.
Google Scholar
[19]
J. Zeng, M.D. Xin, K.W. Li, et al.: J. Phys. Chem. C Vol. 112 (2008), p.4159.
Google Scholar
[20]
D.L. Zhang: Prog. Mater. Sci. Vol. 49 (2004), p.537.
Google Scholar
[21]
N. Nikolic, Z. Marinkovic, T. Sreckovic: J. Mater. Sci. Vol. 39 (2004), p.5239.
Google Scholar