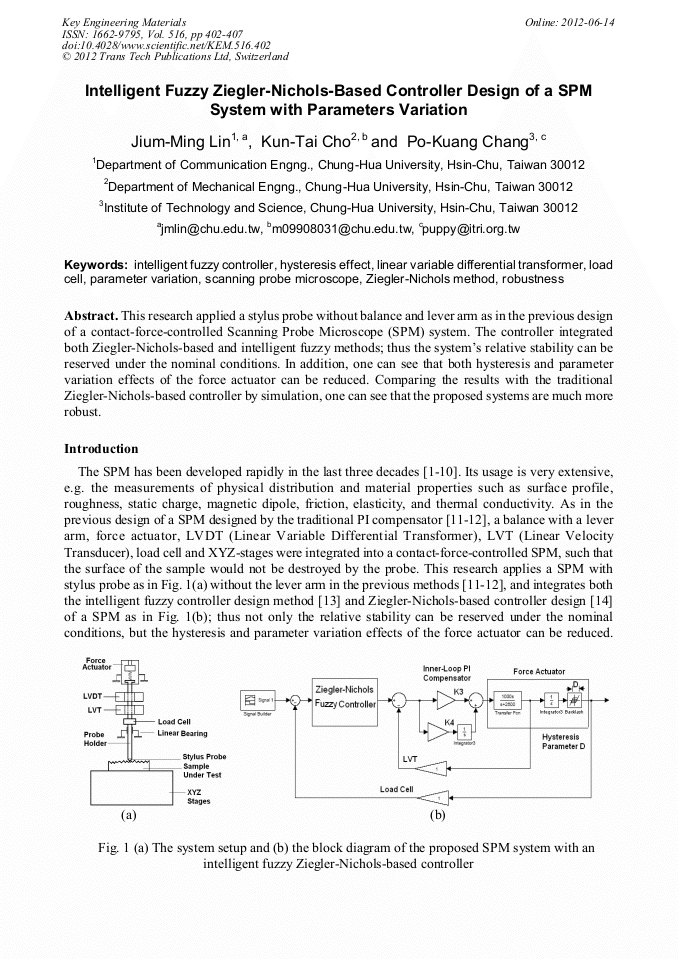
[1]
D. G. Chetwyud, X. Liu, S.T. Smith, A controlled-force stylus displacement probe, Precis. Eng. 19 (1996), 105-111.
Google Scholar
[2]
X. Liu, D.G. Chetwyud, S.T. Smith, W. Wang, Improvement of the fidelity of surface measurement by active damping control, Meas. Sci. Technol. 4 (1993), 1330-1340.
DOI: 10.1088/0957-0233/4/12/004
Google Scholar
[3]
M. Bennett, J.H. Dancy, Stylus profiling instrument for measuring statistical properties of smooth optical surfaces, Appl. Optics 20 (1981) 1785-1802.
DOI: 10.1364/ao.20.001785
Google Scholar
[4]
D.G. Chetwyud, X. Liu, S.T. Smith, Signal fidelity and tracking force in stylus profilometry, J. Mach. Tool. Manuf. 32 (1992) 239-245.
Google Scholar
[5]
G. Neubauer, Force microscopy with a bidirectional capacitor sensor, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 61 (1990) 2296-2308.
Google Scholar
[6]
M. Bennett, J.H. Dancy, Stylus profiling instrument for measuring statistical properties of smooth optical surfaces, Appl. Optics 20 (1981), 1785-1802.
DOI: 10.1364/ao.20.001785
Google Scholar
[7]
J.I. Seeger, S.B. Crary, Stabilization of statistically actuated mechanical devices, Electro-transducers '97 (1981), Chicago, IL, 1133.
Google Scholar
[8]
G. Haugstad, R.R. Jones, Mechanisms of dynamic force microscopy on polyvinyl alcohol: region-specific non-contact and intermittent contact regimes, Ultra microscopy, 76 (1999) 77-86.
DOI: 10.1016/s0304-3991(98)00073-4
Google Scholar
[9]
V.V. Prokhorov, S.A. Saunin, Probe-surface interaction mapping in amplitude modulation atomic force microscopy by integrating amplitude-distance and amplitude-frequency curves, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91 (2007) 1063-1065.
DOI: 10.1063/1.2756271
Google Scholar
[10]
Information on http: /metrologyinternational. talkware. co. uk/blog/Nano2D3Dsurfaceprofiling.
Google Scholar
[11]
J. M. Lin, C. C. Lin, Profiler design with multi-sensor data fusion methods, SICE Annual Conference (2007) 710-715.
DOI: 10.1109/sice.2007.4421074
Google Scholar
[12]
P. K. Chang, J. M. Lin, Scanning probe microscope system design with linear velocity transducer for feedback compensation, SICE Annual Conference (2008) 2382-2387.
DOI: 10.1109/sice.2008.4655063
Google Scholar
[13]
H. Zhang, D. Liu, Fuzzy Modelling & Fuzzy Control, New York: Springer-Verlag, (2006).
Google Scholar
[14]
J. G. Ziegler, N. B. Nichols, Optimum settings for automatic controllers, Trans. ASME, 64 (1942) 759-768.
DOI: 10.1115/1.4019269
Google Scholar