p.364
p.369
p.375
p.380
p.389
p.395
p.401
p.406
p.412
A Study on the Magnesium Sulfate Resistance of Garnet Fiber Concrete
Abstract:
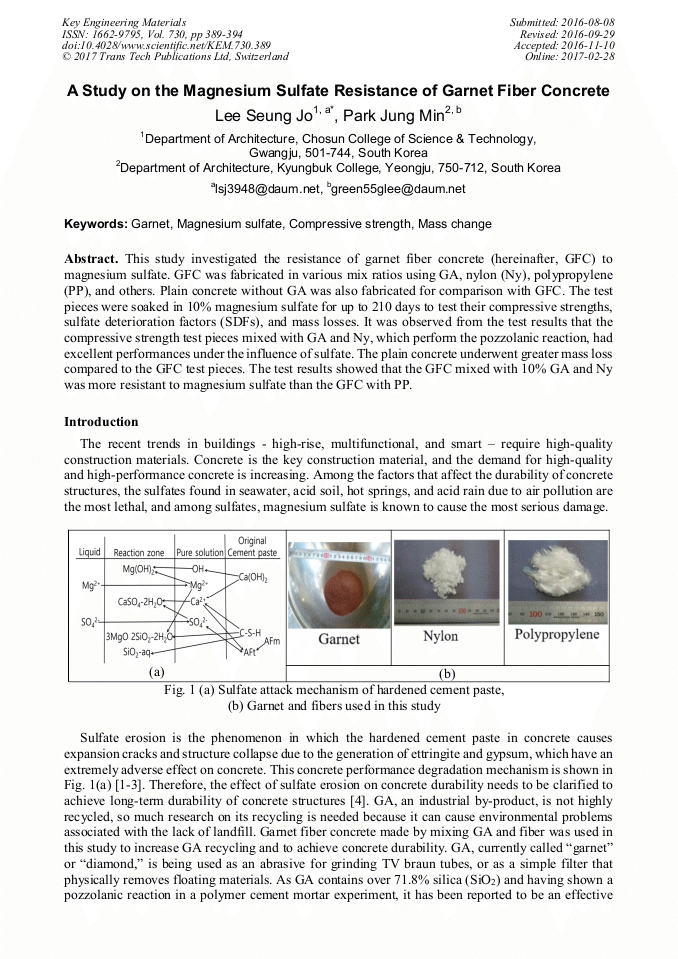
This study investigated the resistance of garnet fiber concrete (hereinafter, GFC) to magnesium sulfate. GFC was fabricated in various mix ratios using GA, nylon (Ny), polypropylene (PP), and others. Plain concrete without GA was also fabricated for comparison with GFC. The test pieces were soaked in 10% magnesium sulfate for up to 210 days to test their compressive strengths, sulfate deterioration factors (SDFs), and mass losses. It was observed from the test results that the compressive strength test pieces mixed with GA and Ny, which perform the pozzolanic reaction, had excellent performances under the influence of sulfate. The plain concrete underwent greater mass loss compared to the GFC test pieces. The test results showed that the GFC mixed with 10% GA and Ny was more resistant to magnesium sulfate than the GFC with PP.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
389-394
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
February 2017
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2017 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: