p.165
p.174
p.182
p.189
p.197
p.207
p.216
p.227
p.235
Seismic Requirements for the Welding and Inspection of the K-Area in Hot Rolled Products to AS/NZS 3679.1
Abstract:
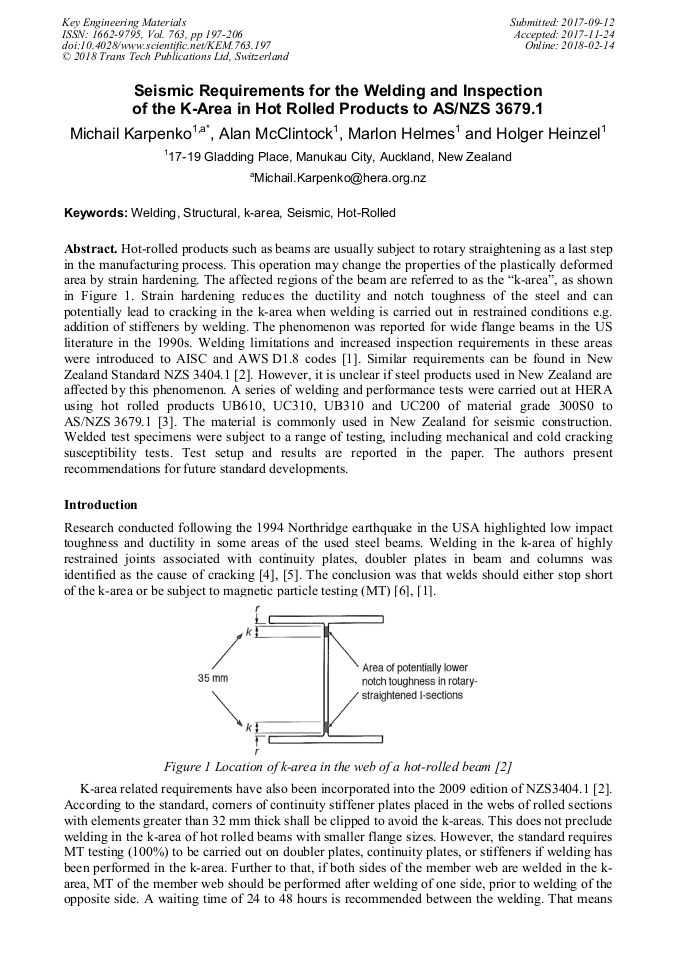
Hot-rolled products such as beams are usually subject to rotary straightening as a last step in the manufacturing process. This operation may change the properties of the plastically deformed area by strain hardening. The affected regions of the beam are referred to as the “k-area”, as shown in Figure 1. Strain hardening reduces the ductility and notch toughness of the steel and can potentially lead to cracking in the k-area when welding is carried out in restrained conditions e.g. addition of stiffeners by welding. The phenomenon was reported for wide flange beams in the US literature in the 1990s. Welding limitations and increased inspection requirements in these areas were introduced to AISC and AWS D1.8 codes [1]. Similar requirements can be found in New Zealand Standard NZS 3404.1 [2]. However, it is unclear if steel products used in New Zealand are affected by this phenomenon. A series of welding and performance tests were carried out at HERA using hot rolled products UB610, UC310, UB310 and UC200 of material grade 300S0 to AS/NZS 3679.1 [3]. The material is commonly used in New Zealand for seismic construction. Welded test specimens were subject to a range of testing, including mechanical and cold cracking susceptibility tests. Test setup and results are reported in the paper. The authors present recommendations for future standard developments.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
197-206
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
February 2018
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2018 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: