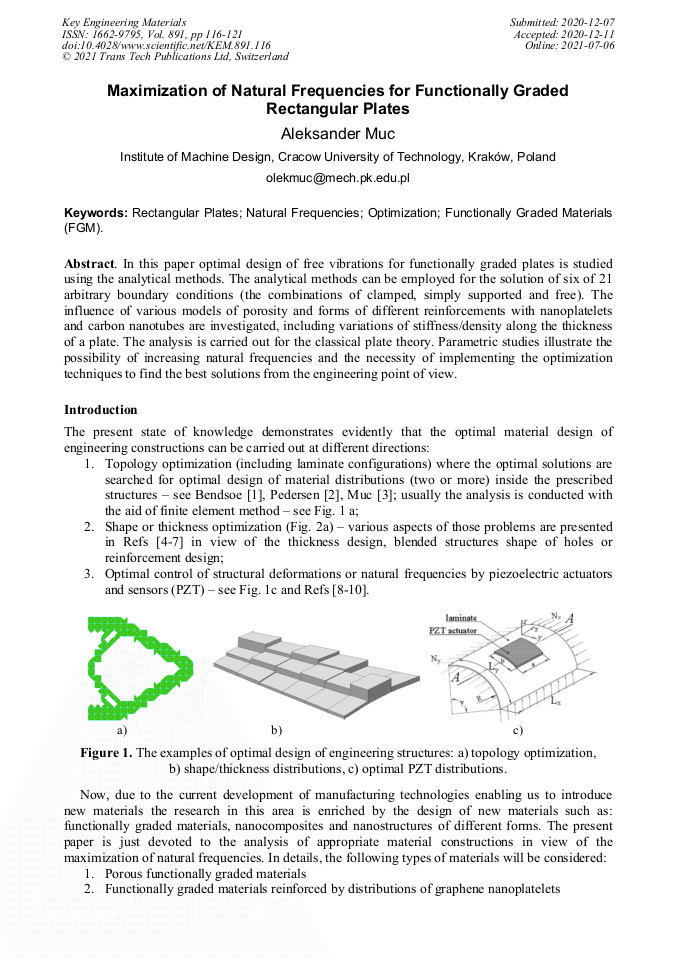
[1]
Bendsøe, M.P., Sigmund O., Topology Optimization. Theory, Methods and Applications, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, (2004).
Google Scholar
[2]
Pedersen P., Design for minimum stress concentration – some practical aspects, Structural Optimization (Rozvany, G.I.N., Karihaloo, B.L., eds), Kluwer, Dordrecht, 1988, pp.225-232.
DOI: 10.1007/978-94-009-1413-1_29
Google Scholar
[3]
Muc, A., Gurba, W., Genetic algorithms and finite element analysis in optimization of composite structures (2001) Composite Structures, 54 (2-3), pp.275-281.
DOI: 10.1016/s0263-8223(01)00098-8
Google Scholar
[4]
Muc, A., Optimal design of composite multilayered plated and shell structures (2007) Thin-Walled Structures, 45 (10-11), pp.816-820.
DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2007.08.042
Google Scholar
[5]
Muc, A., Ulatowska, A., Local fibre reinforcement of holes in composite multilayered plates, (2012) Composite Structures, 94 (4), pp.1413-1419.
DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.11.017
Google Scholar
[6]
Muc, A., Effectiveness of optimal design with respect to computational models for laminated composite structures weakened by holes, (1998) Structural Optimization, 16 (1), pp.58-67.
DOI: 10.1007/bf01214000
Google Scholar
[7]
Muc, A., Design of blended/tapered multilayered structures subjected to buckling constraints (2018) Composite Structures, 186, pp.256-266.
DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.12.001
Google Scholar
[8]
Muc, A., Kędziora, P., Optimal design of smart laminated composite structures, (2010) Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 25 (4), pp.272-280.
DOI: 10.1080/10426910903426463
Google Scholar
[9]
Kędziora, P., Muc, A., Optimal shapes of PZT actuators for laminated structures subjected to displacement or eigenfrequency constraints, (2012) Composite Structures, 94 (3), pp.1224-1235.
DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.11.019
Google Scholar
[10]
Muc, A., Kędziora, P., Stawiarski, A., Buckling enhancement of laminated composite structures partially covered by piezoelectric actuators, (2019) European Journal of Mechanics, A/Solids, 73, pp.112-125.
DOI: 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2018.07.002
Google Scholar
[11]
Trung Thanh Tran, Quoc-Hoa Pham, Trung Nguyen-Thoi, Static and free vibration analyses of functionally graded porous variable-thickness plates using an edge-based smoothed finite element method, Defence Technology, https://doi.org/10.1016 /j. dt. 2020.06.001.
DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2020.06.001
Google Scholar
[12]
M.T. Song, J. Yang, S. Kitipornchai, Buckling and postbuckling of biaxially compressed functionally graded multilayer graphene nanoplatelet-reinforced polymer composite plates, (2017) Int. J. Mech. Sci. 131 p.345–355.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.07.017
Google Scholar
[13]
Z.X. Lei, L.W. Zhang, K.M. Liew, Free vibration analysis of laminated FG-CNT reinforced composite rectangular plates using the kp-Ritz method, (2015) Composite Structures, 127, p.245–259.
DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.03.019
Google Scholar
[14]
Leissa AW, Free vibrations of rectangular plates, Journal of Sound and Vibration (1973) 31(3), pp.257-293.
DOI: 10.1016/s0022-460x(73)80371-2
Google Scholar