p.952
p.957
p.964
p.971
p.978
p.984
p.990
p.997
p.1003
High-Temperature Tribological Properties of ReB2-Based Ceramic/Si3N4 Sliding Pairs
Abstract:
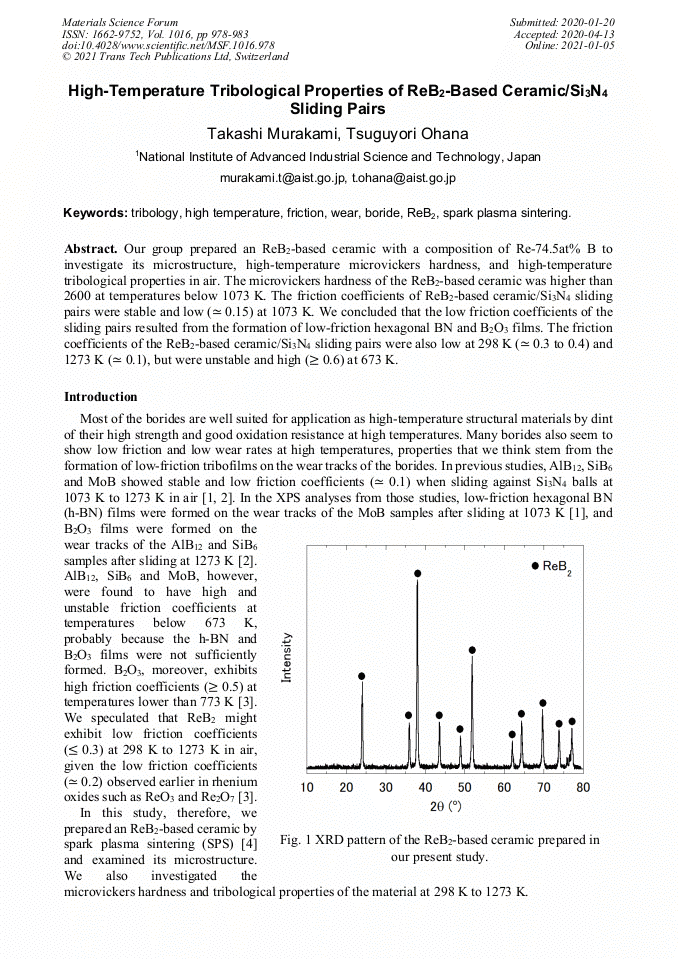
Our group prepared an ReB2-based ceramic with a composition of Re-74.5at% B to investigate its microstructure, high-temperature microvickers hardness, and high-temperature tribological properties in air. The microvickers hardness of the ReB2-based ceramic was higher than 2600 at temperatures below 1073 K. The friction coefficients of ReB2-based ceramic/Si3N4 sliding pairs were stable and low (≃ 0.15) at 1073 K. We concluded that the low friction coefficients of the sliding pairs resulted from the formation of low-friction hexagonal BN and B2O3 films. The friction coefficients of the ReB2-based ceramic/Si3N4 sliding pairs were also low at 298 K (≃ 0.3 to 0.4) and 1273 K (≃ 0.1), but were unstable and high ( 0.6) at 673 K.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
978-983
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
January 2021
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2021 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: