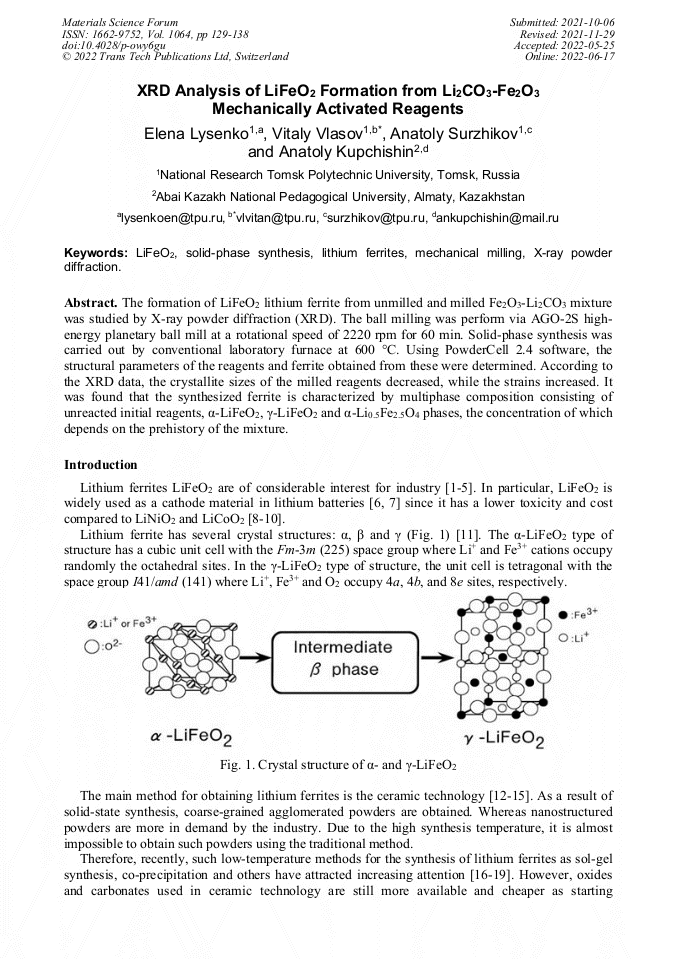
[1]
M. Barre, M. Catti. Neutron diffraction study of the β' and γ phases of LiFeO2, J. Solid St. Ch., 182 (2009) 2549-2554.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2009.06.029
Google Scholar
[2]
Y.T. Lee, C.S. Yoon, Y.S. Lee, Y.-K. Sun. Synthesis and structural changes of LixFeyOz material prepared by a solid-state method, J. Power Sour. 134 (2004) 88-94.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.02.001
Google Scholar
[3]
Y.S. Lee, C.S. Yoon, Y.K. Sun, K Kobayakawa, Y. Sato. Synthesis of nano-crystalline LiFeO2 material with advanced battery performance, Elect. Com. 4 (2002) 727-731.
DOI: 10.1016/s1388-2481(02)00436-8
Google Scholar
[4]
A.E. Abdel-Ghany, A. Mauger, H. Groult, K. Zaghib, C.M. Julien. Structural properties and electrochemistry of α-LiFeO2, J. Power Sour. 197 (2012) 285-291.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.09.054
Google Scholar
[5]
A.K. Tangra, G.S. Lotey. Synthesis and investigation of structural, optical, magnetic, and biocompatibility properties of nanoferrites AFeO2, Curr. Appl. Ph. 27 (2021) 103-116.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cap.2021.04.011
Google Scholar
[6]
R. Kanno, T. Shirane, Y. Kawamoto, Y. Takeda, M. Takano, M. Ohashi, Y. Yamaguchi. Synthesis, structure, and electrochemical properties of a new lithium iron oxide, LiFeO2, with a corrugated layer structure, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143 (1996) 2435-2442.
DOI: 10.1149/1.1837027
Google Scholar
[7]
T. Matsumura, R. Kanno, Y. Inaba, Y. Kawamoto, M. Takano. Synthesis, structure, and electrochemical properties of a new cathode material LiFeO2, with a tunnel structure, J. Electrochem. Soc. 149 (2002) A1509–A1513.
DOI: 10.1149/1.1516769
Google Scholar
[8]
Y. Sakurai, H. Arai, S. Okada, J. Yamaki. Low temperature synthesis and electrochemical characterization of LiFeO2 cathodes, J. Power Sour. 68 (1997) 711-715.
DOI: 10.1016/s0378-7753(96)02579-7
Google Scholar
[9]
J.R. Dahn, U. Von Sacken, C.A. Michal. Structure and electrochemistry of Li1 ± yNiO2 and a new Li2NiO2 phase with the Ni(OH)2 structure, Sol. St. Ion. 44 (1990) 87-97.
DOI: 10.1016/0167-2738(90)90049-w
Google Scholar
[10]
Y. Sakurai, H. Arai, J. Yamaki. Preparation of electrochemically active α-LiFeO2 at low temperature, Solid State Ion. 29 (1998) 113-115.
DOI: 10.1016/s0167-2738(98)00363-4
Google Scholar
[11]
M. Tabuchi, S. Tsutsui, C. Masquelier, R. Kanno, K. Ado, I. Matsubara, S. Nasu, H. Kageyama. Effect of Cation Arrangement on the Magnetic Properties of Lithium Ferrites (LiFeO2) Prepared by Hydrothermal Reaction and Post-annealing Method, J. Solid St. Ch., 140 (1998) 159-167.
DOI: 10.1006/jssc.1998.7725
Google Scholar
[12]
G.A. El-Shobaky, A.A. Ibrahim. Solid-solid interactions between ferric oxide and lithium carbonate and the thermal stability of the lithium ferrites produced, Thermoch. Acta. 118 (1987) 151-158.
DOI: 10.1016/0040-6031(87)80079-5
Google Scholar
[13]
S.K. Rakshit, S.C. Parida, Y.P. Naik, V. Venugopal. Thermodynamic studies on lithium ferrites, J. Solid State Chem. 184 (2011) 1186-1194.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2011.03.033
Google Scholar
[14]
A.P. Surzhikov, A.M. Pritulov, E.N. Lysenko, V.A. Vlasov, E.A. Vasendina, A.V. Malyshev. Analysis of the phase composition and homogeneity of ferrite lithium-substituted powders by the thermomagnetometry method, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 112 (2013) 739-745.
DOI: 10.1007/s10973-012-2618-6
Google Scholar
[15]
S.S. Teixeira, M.P.F. Grac, L.C. Costa. Dielectric, morphological and structural properties of lithium ferrite powders prepared by solid state method, J. Noncryst. Solids. 358 (2012) 1924-1929.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2012.06.003
Google Scholar
[16]
B.S. Randhawa, H.S. Dosanjh, N. Kumar. Synthesis of lithium ferrite by precursor and combustion methods: a comparative study, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 274 (2007) 581-591.
DOI: 10.1007/s10967-006-6924-y
Google Scholar
[17]
V. Verma, V. Pandey, R.P. Aloysius, S. Annapoorni, R.K. Kotanala. Comparative study of structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Li0.5Fe2.5O4 prepared by various methods, Phys B. 404 (2009) 2309-2314.
DOI: 10.1016/j.physb.2009.04.034
Google Scholar
[18]
G. Aravind, M. Raghasudha, D.M. Ravinder, R. Manivel, S.S. Meena, P. Bhatt. Study of structural and magnetic properties of Li–Ni nanoferrites synthesized by citrate-gel auto combustion method, Ceram. Int. 42 (2016) 2941-2950.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.077
Google Scholar
[19]
M. Tabuchi, K. Ado, H. Sakaebe, C. Masquelier, H. Kageyama, O. Nakamura. Preparation of AFeO2 (A = Li, Na) by hydrothermal method, Solid State Ion. 79 (1995) 220-226.
DOI: 10.1016/0167-2738(95)00065-e
Google Scholar
[20]
V. Berbenni, G. Bruni, C. Milanese, A. Girella, A. Marini. Synthesis and characterization of LaFeO3 powders prepared by a mixed mechanical/thermal processing route, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 133 (2018) 413-419.
DOI: 10.1007/s10973-017-6878-z
Google Scholar
[21]
T.T. Parlak, F. Apaydin, K. Yildiz. Formation of SrTiO3 in mechanically activated SrCO3–TiO2 system, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 127 (2017) 63-69.
DOI: 10.1007/s10973-016-5385-y
Google Scholar
[22]
V. Mihalache. Thermal analysis of ball-milled Fe–14Cr–3 W–0.4Ti–0.25Y2O3 ferritic steel powder, J Therm. Anal. Calorim. 124 (2016) 1179-1192.
DOI: 10.1007/s10973-016-5304-2
Google Scholar
[23]
V. Berbenni, A. Marini, P. Matteazzi, R. Ricceri, N.J. Welham. Solid-state formation of lithium ferrites from mechanically activated Li2CO3–Fe2O3 mixtures, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23 (2003) 527-536.
DOI: 10.1016/s0955-2219(02)00150-4
Google Scholar
[24]
H.M. Widatallah, C. Johnson, F.J. Berry. The influence of ball milling and subsequent calcination on the formation of LiFeO2, J. Mater. Sci. 37 (2002) 4621-4625.
Google Scholar
[25]
M. Kavanlooee, B. Hashemi, H. Maleki-Ghaleh, J. Kavanlooee. Effect of annealing on phase evolution, microstructure, and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline ball-milled LiZnTi ferrite, J. Electron. Mater. 41 (2012) 3082-3086.
DOI: 10.1007/s11664-012-2235-y
Google Scholar
[26]
S.H. Gee, Y.K. Hong, M.H. Park, D.W. Erickson, P.J. Lamb. Synthesis of nanosized (Li0.5xFe0.5xZn1-x)Fe2O4 particles and magnetic properties, J. Appl. Phys. 91 (2002) 7586–7588.
Google Scholar
[27]
H.M. Widatallah, X.L. Ren, I.A. Al-Omari. The influence of TiO2 polymorph, mechanical milling and subsequent sintering on the formation of Ti-substituted spinel-related Li0.5Fe2.5O4, J. Mater. Sci. 41 (2006) 6333-6338.
DOI: 10.1007/s10853-006-0721-4
Google Scholar
[28]
A.P. Surzhikov, E.N. Lysenko, A.V. Malyshev, A.M. Pritulov, O.G. Kazakovskaya Influence of mechanical activation of initial reagents on synthesis of lithium ferrite, Russ. Phys. J. 6 (2012) 672-677.
DOI: 10.1007/s11182-012-9865-7
Google Scholar
[29]
A.P. Surzhikov, E.N. Lysenko, V.A. Vlasov, A.V. Malyshev, E.V. Nikolaev. Thermal analysis study of solid-phase synthesis of zinc- and titanium-substituted lithium ferrites from mechanically activated reagents, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 122 (2015) 1347-1353.
DOI: 10.1007/s10973-015-4849-9
Google Scholar
[30]
E.N. Lysenko, E.V. Nikolaev, V.A. Vlasov, A.P. Surzhikov, Microstructure and reactivity of Fe2O3-Li2CO3-ZnO ferrite system ball-milled in a planetary mill, Thermochim. Acta. 664 (2018) 100-107.
DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2018.04.015
Google Scholar
[31]
E.N. Lysenko, A.P. Surzhikov, E.V. Nikolaev, V.A. Vlasov. Thermal analysis study of LiFeO2 formation from Li2CO3–Fe2O3 mechanically activated reagents, J. Therm. Anal. Calor. 134 (2018) 81-87.
DOI: 10.1007/s10973-018-7113-2
Google Scholar
[32]
V. Berbenni, A. Marini, P. Matteazzi, R. Ricceri, N.J. Welham. Solid-state formation of lithium ferrites from mechanically activated Li2CO3–Fe2O3 mixtures, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23 (2003) 527-536.
DOI: 10.1016/s0955-2219(02)00150-4
Google Scholar