p.788
p.794
p.801
p.807
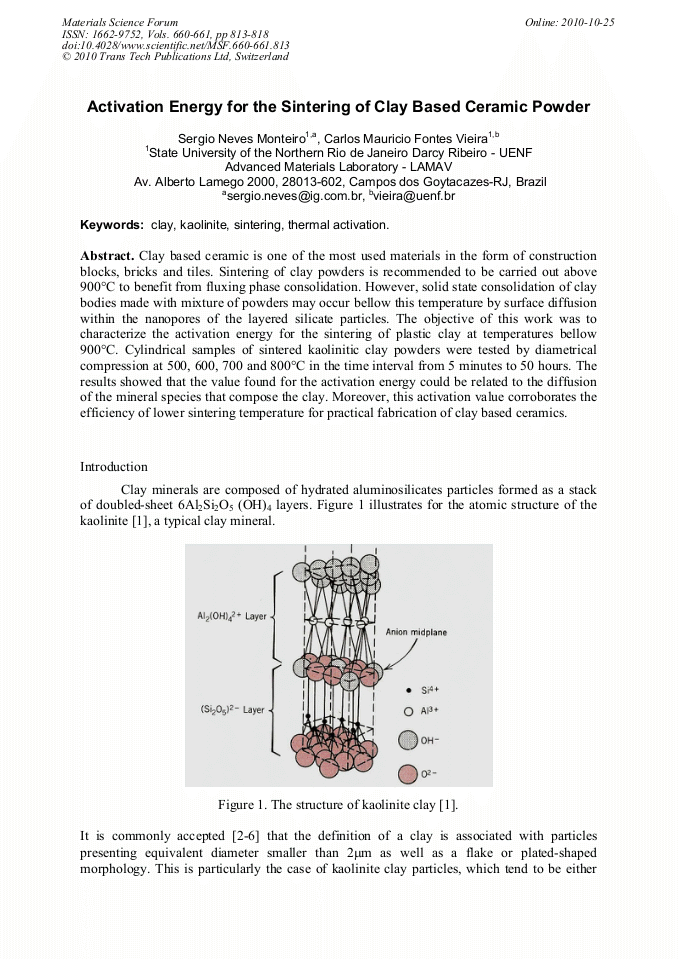
p.813
p.819
p.826
p.832
p.837
Activation Energy for the Sintering of Clay Based Ceramic Powder
Abstract:
Clay based ceramic is one of the most used materials in the form of construction blocks, bricks and tiles. Sintering of clay powders is recommended to be carried out above 900°C to benefit from fluxing phase consolidation. However, solid state consolidation of clay bodies made with mixture of powders may occur bellow this temperature by surface diffusion within the nanopores of the layered silicate particles. The objective of this work was to characterize the activation energy for the sintering of plastic clay at temperatures bellow 900°C. Cylindrical samples of sintered kaolinitic clay powders were tested by diametrical compression at 500, 600, 700 and 800°C in the time interval from 5 minutes to 50 hours. The results showed that the value found for the activation energy could be related to the diffusion of the mineral species that compose the clay. Moreover, this activation value corroborates the efficiency of lower sintering temperature for practical fabrication of clay based ceramics.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
813-818
Citation:
Online since:
October 2010
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2010 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: