p.87
p.91
p.100
p.106
p.115
p.119
p.125
p.130
p.136
Using Shear Wave Velocity to Assess the Stiffness of Soil-Cement-Fly Ash
Abstract:
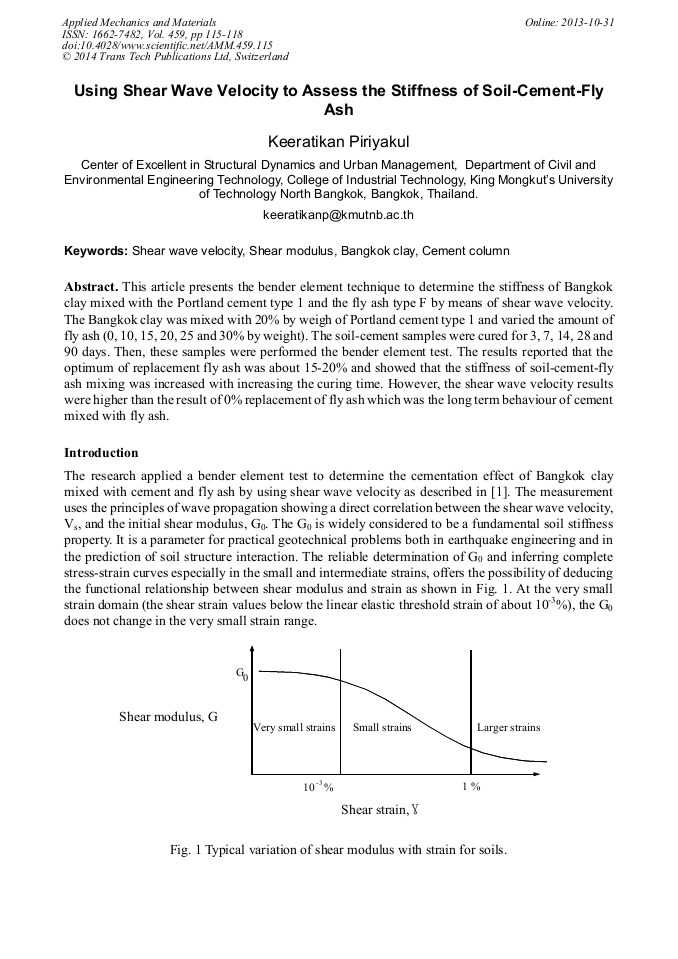
This article presents the bender element technique to determine the stiffness of Bangkok clay mixed with the Portland cement type 1 and the fly ash type F by means of shear wave velocity. The Bangkok clay was mixed with 20% by weigh of Portland cement type 1 and varied the amount of fly ash (0, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30% by weight). The soil-cement samples were cured for 3, 7, 14, 28 and 90 days. Then, these samples were performed the bender element test. The results reported that the optimum of replacement fly ash was about 15-20% and showed that the stiffness of soil-cement-fly ash mixing was increased with increasing the curing time. However, the shear wave velocity results were higher than the result of 0% replacement of fly ash which was the long term behaviour of cement mixed with fly ash.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
115-118
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
October 2013
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: