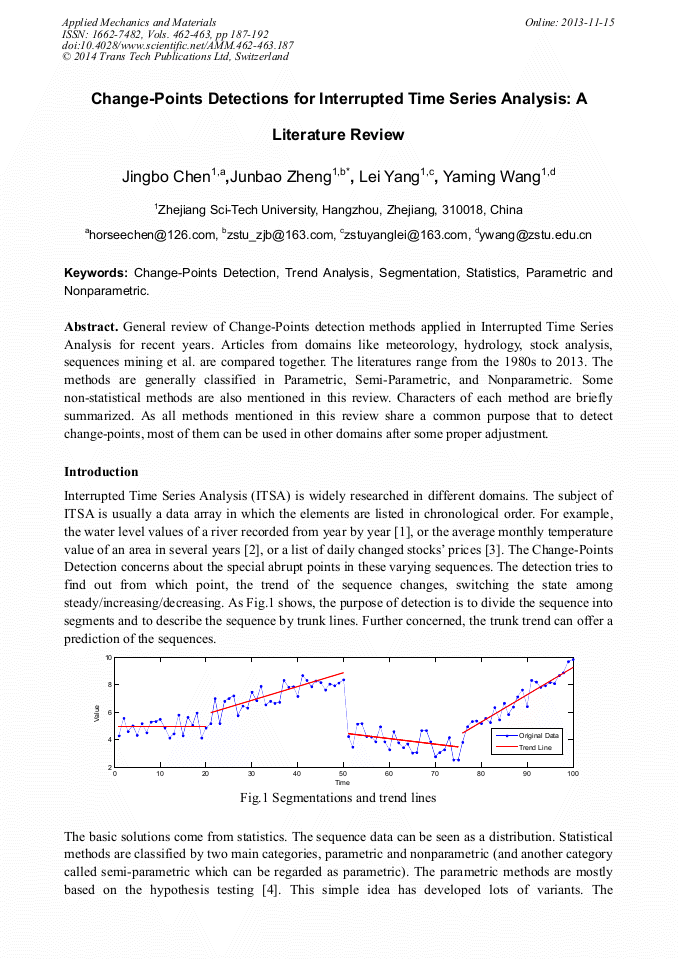
[1]
S. Yue and C. Wang: The Mann-Kendall Test Modified by Effective Sample Size to Detect Trend in Serially Correlated Hydrological Series: Water Resouces Management, Vol. 18 (2004), pp.201-218.
DOI: 10.1023/b:warm.0000043140.61082.60
Google Scholar
[2]
R. Lund and J. Reeves: Detection of Undocumented Changepoints: A Revision of the Two-Phase Regression Model: J. Climate, Vol. 15-17(2002), pp.2547-2554.
DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<2547:doucar>2.0.co;2
Google Scholar
[3]
H.B. Mann: Nonparametric tests against trend: Econometrica, Vol. 13(1945), pp.245-259.
DOI: 10.2307/1907187
Google Scholar
[4]
F. Osorio and M. Galea: Detection of a change-point in student-t linear regression models: Statistical Papers, Vol. 45 (2005), pp.31-48.
DOI: 10.1007/s00362-005-0271-x
Google Scholar
[5]
E. S. Page: Cumulative sum schemes using gauging: Technometrics, Vol. 4-1(1962), pp.97-109.
DOI: 10.1080/00401706.1962.10489990
Google Scholar
[6]
T. L. Lai: Sequential Changepoint Detection in Quality Control and Dynamical Systems: J. R. Statist. Soc. B, Vol. 57-4 (1995), pp.613-658.
Google Scholar
[7]
D. Siegumund and E. S. Venkatraman: Using The Generalized Likelihood Ratio Statistic for Sequential Detection of a Change-Point: The Annals of Statistics, Vol. 23-1(1995), pp.255-271.
DOI: 10.1214/aos/1176324466
Google Scholar
[8]
A. R. Solow: Testing for Climate Change: An Application of the Two-Phase Regression Model: J. Climate Appl. Meteor, 26 (1987), 1401–1405.
DOI: 10.1175/1520-0450(1987)026<1401:tfccaa>2.0.co;2
Google Scholar
[9]
Z. Guan: Semiparametric tests for change-points with epidemic alternatives: Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, Vol. 137(2007), pp.1748-1764.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jspi.2006.05.006
Google Scholar
[10]
B. Cai, Andrew B Lawson, Suzanne McDermott et al.: A Bayesian semi-parametric approach with change points for spatial ordinal data: Statistical Methods in Medical Research, Vol. 0-0(2012), pp.1-15.
DOI: 10.1177/0962280212463415
Google Scholar
[11]
B. Brodsky and B. Darkhovsky: Asymptotically optimal methods of change-point detection for composite hypotheses: Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference: Vol. 133(2005), pp.123-138.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jspi.2004.01.007
Google Scholar
[12]
P. Yang, G. Dumont and J. Lim et al.: Adaptive Change Point Detection for Respiratory Variables: 27th Annual International Conference of the. IEEE (2005), pp.780-783.
DOI: 10.1109/iembs.2005.1616531
Google Scholar
[13]
D. C. Carslaw, K. Ropkins and M. C. Bell: Change-Point Detection of Gaseous and Particulate Traffic-Related Pollutants at a Roadside Location: Environ. Sci. Technol. Vol. 40 (2006), pp.6912-6918.
DOI: 10.1021/es060543u
Google Scholar
[14]
B. Brodsky and B. Darkhovsky: Sequential change-point detection for mixing random sequences under composite hypotheses: Statistical Inference for Stochastic Processes, Vol. 11-1 (2008), pp.35-54.
DOI: 10.1007/s11203-006-9004-6
Google Scholar
[15]
V. M. De Oca, D. R. Jeske, Q. Zhang et al.: A cusum change-point detection algorithm for non-stationary sequences with application to data network surveillance: The Journal of Systems and Software, Vol. 83(2010), pp.1288-1297.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.02.006
Google Scholar
[16]
M.G. Kendall: Rank Correlation Methods (Charles Griffin & Company published, London 1970).
Google Scholar
[17]
K. H. Hamed and A. R. Rao: A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data: Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 204 (1998), pp.182-196.
DOI: 10.1016/s0022-1694(97)00125-x
Google Scholar
[18]
S. Yue, P. Pilon and G. Cavadias: Power of the Mann-Kendall and Spearman's rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series: Journal of Hydrology, Vol. 259 (2002), pp.254-271.
DOI: 10.1016/s0022-1694(01)00594-7
Google Scholar
[19]
G. Chattopadhyay, P. Chakraborthy and S. Chattopadhyay: Mann-Kendall trend analysis of tropospheric ozone and its modeling using ARIMA: Theor Appl. Climatol, Vol. 110 (2012), pp.321-328.
DOI: 10.1007/s00704-012-0617-y
Google Scholar
[20]
M. Shadmani, S. Marofi and M. Roknian: Trend Analysis in Reference Evapotranspiration Using Mann-Kendall and Spearman's Rho Tests in Arid Regions of Iran: Water Resour Manage, Vol. 26 (2012), pp.211-224.
DOI: 10.1007/s11269-011-9913-z
Google Scholar
[21]
M. Gocic and S. Trajkovic: Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen's slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia: Global and Planetary change, Vol. 100 (2013), pp.172-182.
DOI: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.10.014
Google Scholar
[22]
R. L. Carter and B. J. N. Blight: A Bayesian Change-Point Problem with an Application to the Prediction and Detection of Ovulation in Women: Biometrics, Vol. 37 (1981), pp.743-751.
DOI: 10.2307/2530156
Google Scholar
[23]
B.K. Ray and R.S. Tsay: Bayesian methods for change-point detection in long-range dependent processes: Journal of Time Series Analysis, Vol. 23-6(2002), pp.687-705.
DOI: 10.1111/1467-9892.00286
Google Scholar
[24]
D. Leonte, D. J. Nott and W. T. M. Dunsmuir: Smoothing and Change Point Detection for Gamma Ray Count Data: Mathematical Geology, Vol. 35-2 (2003), pp.175-194.
Google Scholar
[25]
P. Muller and F. A. Quintana: Nonparametric Bayesian Data Analysis: Statistical Science, Vol. 19-1 (2004), pp.95-110.
Google Scholar
[26]
Y. S. Son and S. W. Kim: Bayesian single change point detection in a sequence of multivariate normal observations: Statistics, Vol. 39-5 (2005), pp.373-387.
DOI: 10.1080/02331880500315339
Google Scholar
[27]
E. Ruggieri: A Bayesian approach to detecting change points in climatic records: Int. J. Climatol. , Vol. 33 (2013), pp.520-528.
DOI: 10.1002/joc.3447
Google Scholar
[28]
A. Jann: Multiple Change-Point Detection with a Genetic Algorithm: Soft Computing, Vol. 4 (2000), pp.68-75.
DOI: 10.1007/s005000000049
Google Scholar
[29]
Y. Tseng, P. Durbin and G. Tzeng: Using a Fuzzy Piecewise Regression Analysis to Predict the Nonlinear Time-Series of Turbulent Flows with Automatic Change-Point Detection: Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, Vol. 67 (2001), pp.81-106.
DOI: 10.1023/a:1014077330409
Google Scholar
[30]
Y. Kawahara, T. Yairi, and K. Machida: Change-Point Detection in Time-Series Data based on Subspace Identification: Seventh IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, (2007), pp.559-564.
DOI: 10.1109/icdm.2007.78
Google Scholar
[31]
M. Fliess, C. Join and M. Mboup: Algebraic Change-Point Detection: AAECC, Vol. 21 (2010), pp.131-143.
DOI: 10.1007/s00200-010-0119-z
Google Scholar